A strategy refers to the set of actions that managers in a company take to increase their company’s performance. The strategy formulation task is the task of selecting strategies, whereas strategy implementation is the task of putting strategies into action.
Strategies can be divided into various categories such as Corporate-level strategies, Global strategies, business-level strategies and functional-level strategies.
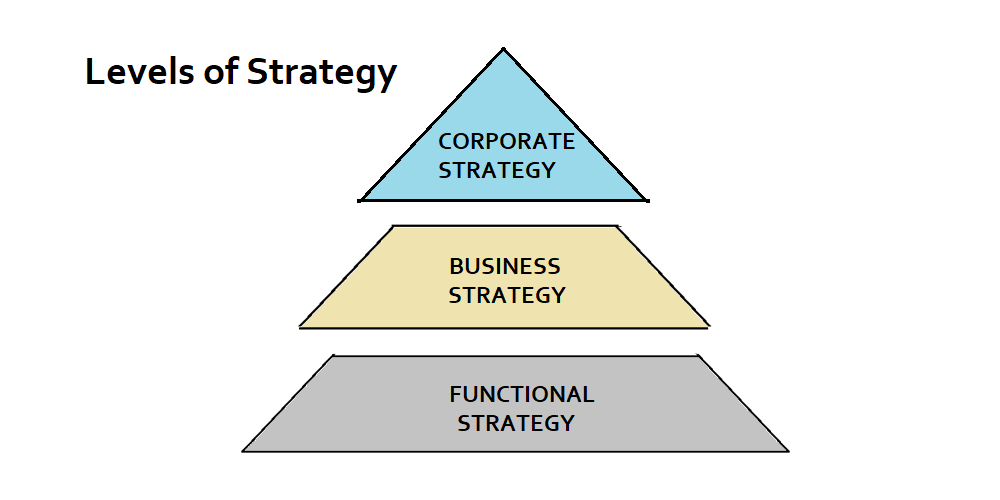
Three Levels of Strategy:
Corporate Level Strategy
This concerns the overall scope of an organisation and includes how value could be added to the organisation as a whole (includes constituent businesses).
These strategies relate to the overall scope of the organization, its structures and financing, and the distribution of resources between its constituent parts (various business units).
Examples: Diversifying from the organisation’s original activities into other activities (e.g. Tesla selling batteries for home use. Reliance getting into retail). Corporate-level strategy is concerned with the overall scope of an organisation and how value is added to the constituent business units.
Business (Competitive) Level Strategy
This concerns how individual businesses should compete in their particular markets (also called competitive strategy).
These strategies relate to how the organization competes in a given market, its approach towards product development, and towards customers.
Marketing and product improvement strategies (e.g. Developing a lower cost, volume car for Tesla).
Business-level strategy is concerned with the way a business seeks to compete successfully in its particular market.
Functional (Operational) Level Strategies
This concerns how the components of an organisation deliver corporate and business level strategies in terms of resources, processes and people, in an effective manner.
These strategies relate to how the various functional (sub units) – marketing, finance, operations, etc. contribute towards higher level strategies.
Example: Tesla’s functional strategies are geared to meeting its investment needs and raising finance.
Functional strategy is concerned with how different parts of the organisation deliver the strategy effectively in terms of managing resources, processes and people.
Levels of Strategy – Tata Example
- Corporate-level Strategy: Tata Group diversifying from areas such as steel & chemicals production to IT consultancy
- Business-level Strategy: Decisions on whether to compete on price or whether to differentiate products & services e.g. Tato Nano competes on price
- Operational Strategy: Constant updating of software & services to meet market needs
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.