Understand the importance of capital investment planning and appraisal. Learn about the key investment appraisal techniques. Understand the importance of human behaviour issues in investment decision making.
Businesses need to make investments and the nature of investment decisions is such that large amounts of resources are often involved and relatively long timescales are involved. It is also often difficult or expensive to bale out of an investment once it is undertaken.
Capital investment appraisal methods are techniques used by businesses and investors to evaluate potential investments and determine whether they are profitable or not. The purpose of capital investment appraisal is to provide decision-makers with a way to compare the costs and benefits of different investment options.
Some common Capital investment appraisal methods include Payback, Discounted Payback, Accounting Rate of Return (ARR). Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Each of these methods has its own strengths and weaknesses, and businesses must choose the method that best suits their needs and goals.
Here’s how investment decisions are managing in most firms.
- Determine investment funds available
- Identify profitable project opportunities
- Refine and classify proposed projects
- Evaluate the proposed project(s)
- Approve the project(s)
- Monitor and control the project(s)
Various Investment Appraisal Methods
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
ARR = (Average annual operating profit) / (Average investment to earn that profit) x 100%.
ARR decision rule
For a project to be acceptable, it must achieve at least a minimum target ARR. Where competing projects exceed the minimum rate, the one with the highest ARR should be selected.
Limitations of ARR
- Ignores the timing of cash flows
- Use of average investment
- Use of accounting profit
- Competing investments
Payback period (PP)
Time taken for initial investment to be repaid out of project net cash inflows.
PP decision rule
Project should have a shorter payback period than the required maximum payback period. If competing projects have payback periods shorter than maximum payback period, the one with the shortest payback period is selected.
Limitations of PP
- Does not take timing of cash flows fully into account
- Ignores cash flows after PP
- Does not take risk fully into account
- Not related to wealth maximisation objective
- Arbitrarily determined target payback period
NPV/ DCF investment appraisal method
Here NPV stands for Net Present value and DCF stands for Discounted cash flow.
This method considers all of the cash flows for each investment opportunity. Makes a logical allowance for the timing of those cash flows.
NPV/DCF takes account of key factors (interest foregone, risk premium, inflation) influencing the return required by investors from a project.
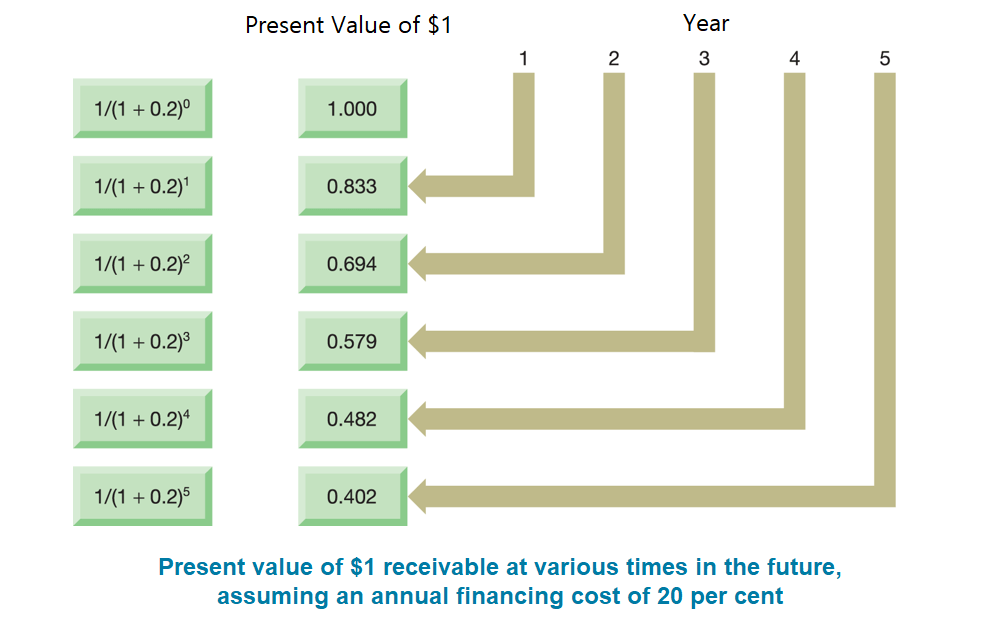
The present value of a cash flow:
PV of the cash flow of year n = actual cash flow of year n divided by (1 + r)n
Why NPV/DCF is better than ARR and PP?
NPV fully addresses each of the following:
- The timing of the cash flows
- The whole of the relevant cash flows
- The objectives of the business
Internal rate of return (IRR)
Internal rate of return (IRR) give a DCF value of $0.
IRR is the discount rate, which, when applied to the future project cash flows, produces a zero NPV.
IRR decision rule
Project must meet a minimum IRR requirement (The opportunity cost of finance). If competing projects exceed minimum IRR requirement, the one with the highest IRR is selected.
Limitations of IRR
- Does not directly address wealth maximisation.
- Ignores the scale of investment.
- Has difficulty with unconventional cash flows.
Investment appraisal in practice
Many surveys have shown the following features:
- Businesses tend to use more than one method
- NPV and IRR have become increasingly popular
- Continued popularity of the PP and ARR methods
- Larger businesses rely more heavily on NPV and IRR than smaller businesses
Where projects are divisible, managers should seek to maximise the present value per dollar of scarce resource
Profitability index (PI) allows ranking of projects based on NPV
PI = (PV of future cash flows) / (Initial outlay)
Inflation and investment appraisal
Two possible approaches (both methods, properly applied, will give the same result):
- Adjust future cash flows for inflation and use a discount rate that is also adjusted for inflation
- Exclude inflation from the future cash flows and use a ‘real’ discount rate that excludes inflation
More Factors to Consider
Investment appraisal and risk
Risk is important because of the long timescales involved and the size of the investment made.
Scenario analysis is a technique that is commonly used to evaluate the potential performance of various investments under different scenarios.
Risk Factors that must be used in scenario analysis that affects the sensitivity of NPV calculations include Annual sales volume, Life of machine, Initial outlay, Operating costs, Financing cost, Sales price.
Behavioural Points
Behavioural aspects in investment decisions are the psychological and emotional factors, such as biases, emotions, and heuristics, that can influence an investor’s decision-making process.
These factors can lead investors to make suboptimal investment decisions, which can result in financial losses.
There are several behavioural aspects in investment decisions.
- Accounting data used is subjective and can be manipulated
- Management may also seek to “empire build”.
- Lack of post completion audit may allow false promises to be made on investment returns
- Managers may compete with each other to get their own investment projects approved rather than seek the best alternative for the company.
As such, it is important for managers to be aware of these behavioral aspects and to take them into account when making investment decisions.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.