The model was developed by McKinsey & Company in the 1980s. Specifically, it was developed by Robert H. Waterman, Jr. and Tom Peters.
- Their research has shown that the success of an organization depends on a number of mutually supporting variables, besides strategy and structure.
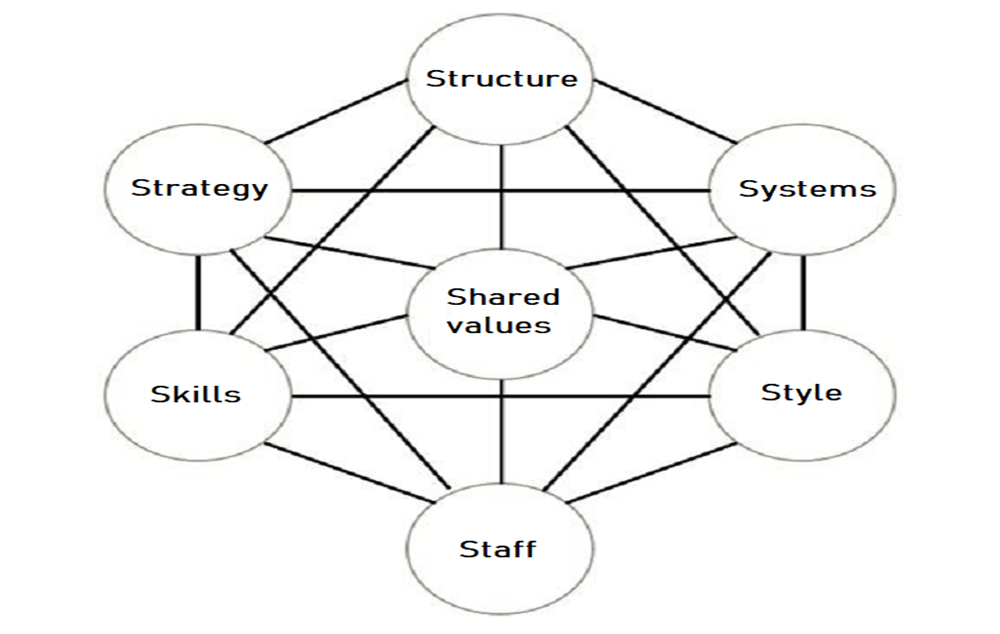
- According to the 7-S framework, effective organizational change is driven by 7-Ss. There are “Hard Ss” and “Soft Ss.”
1. Strategy : is the plan of action an organization prepares in response to, or anticipation of, changes in its external environment. Strategy deals with essentially three questions :
- i) Where the organization is at this moment in time?
- ii) Where the organization wants to be in a particular length of time?
- iii) How to get there?
Strategy is designed to transform the firm from the present position to the new position. It is a plan devised to maintain and build competitive advantage in the market.
2. Structure: It is the organizational arrangements, formal relationships and hierarchy.
- Organizations are structured in a variety of ways, depending on their objectives and culture.
- The structure of the company often dictates the way it operates and performs.
- The businesses have been structured in a hierarchical way with several divisions and departments, each responsible for a specific task such as human resources management, production or marketing.
3. Systems : Every organization has some systems or internal processes to support and implement the strategy and run day-to-day affairs.
- It includes all the rules, regulations, procedures, the daily activities and procedures that staff members engage in to get the job done.
- Earlier the organizations would follow a bureaucraticstyle process model where most decisions were taken at the higher management level, leading to unnecessary delays. Today, organizations have simplified and modernized their processes by innovation and use of new technology to make the decision-making process quicker.
4. Shared Values: All members of the organization share some common fundamental ideas or guiding concepts around which the business is built.
- These values and common goals keep the employees working towards a common goal and are important to keep the team spirit alive.
- The core values of the company are seen in the corporate culture and the general work ethics.
5. Style: All organizations have their own distinct culture and management style.
- It includes the dominant values, beliefs and norms which develop over time and become relatively enduring features of the organizational life.
- It also entails the way managers interact with the employees and the way they spend their time.
6. Staff: Organizations are made up of humans and it’s the people who make the real difference to the success of the organization in the increasingly knowledge-based society.
- The importance of human resources has thus got the central position in the strategy of the organization, away from the traditional model of capital and land.
- All leading organizations put extraordinary emphasis on hiring the best staff, providing them with rigorous training and motivating them to achieve professional excellence.
- This forms the basis of these organizations’ strategy and competitive advantage.
7. Skills: This variable refers to the capabilities of the staff within the organization as a whole.
- It includes the actual skills and competencies of the employees working for the company.
The hard components are the strategy, structure and systems which are normally feasible and easy to identify in an organization as they are normally well documented and seen in the form of tangible objects or reports such as strategy statements, corporate plans, organizational charts and other documents.
The remaining four S’s, however, are more difficult to comprehend.
Limitations of MCKINSEY 7 – S FRAMEWORK
- It ignores the importance of the external environment and depicts only the most crucial elements in this model for explaining the interdependence of the key processes and factors within the organization.
- The model does not explain the concept of organizational effectiveness or performance explicitly.
- The model has been criticized for lacking enough empirical evidences to support their explanation.
- The model is considered to be more of a static kind of model.
- It is rather difficult to assess the degree of fit with accuracy successfully.
- It is criticized for missing out the finer areas in which the actual gaps in conceptualization and execution of strategy may arise.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.