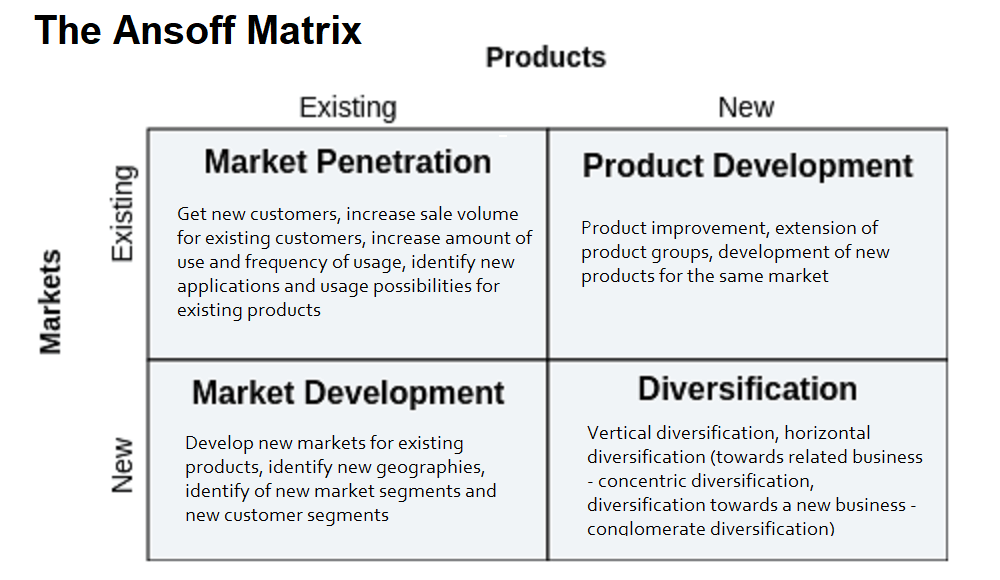
Ansoff Matrix, often referred to as the Product/Market Expansion Grid, is a strategic planning framework used by firms to help plan their growth initiatives. The matrix talks about four different growth alternatives – market penetration, market development, product development and diversification.
The Ansoff matrix is named after Igor Ansoff, who published it in a Harvard Business Review article titled “Strategies for Diversification.”
Ansoff matrix includes four strategies: Market Penetration, Product Development, Market Development, Diversification.
Example of Ansoff Matrix
Example of Starbucks
- Market Penetration (Existing Products, Existing Markets): Loyalty card and reward programme with the help of an app.
- Product Development (New Products, Existing Markets): Starbucks created an instant coffee ‘Via’ brand that customers can buy and drink at home. Starbucks launched a coffee machine
- Market Development (Existing Products, New Markets): Starbucks entering in another country (Starbucks entered India via an alliance with the Tata Group)
- Diversification (New Products, New Markets): Starbucks created new ventures including CDs and movie production operating internationally
Market Penetration
The first quadrant of Ansoff’s Matrix is Market Penetration which involves selling more of the same products and services to the same market. Using this strategy a firm tries to capture a bigger part of the market by selling its existing products in the existing markets.
Market Penetration strategy helps firms generate more sales and acquire more customers and is an essential strategy to gain market dominance, capture more market share, to increase entry barriers for new competitors.
This is a good strategy to adopt in markets that are growing and where consumers have more disposable incomes.
It is also relatively low risk. However, once markets mature and become saturated with other competitors, it becomes increasingly difficult to achieve growth through market penetration.
Market penetration is usually achieved through different marketing activities such as:
- Developing social media strategies and use of influencers.
- Introducing loyalty schemes.
- Up selling or cross marketing to developing competitive pricing strategies to increase usage.
- Engaging in marketing/ promotional campaigns or placing more emphasis on personal selling in commercial markets.
Product Development
In the second quadrant (product development strategy), a firm extends its product portfolio by developing more products and tries reaching more consumer target segments in existing markets.
Product or service innovation is a key characteristic of successful growth SMEs.
As part of this strategy, a firm creates new products but it may also improve the existing products.
Firms may launch completely new products or services because of emerging market opportunities, or to replace existing products or to market them alongside existing products. It might also involve development or extensions of existing products or services. Firms may also introduce ‘me too’ products in response to the activity of competitors.
In order to use this strategy, it is important for the company to have a good understanding of the needs of the consumers, it needs to have differentiated products.
Market Development
Using Market development strategy, a firm enters new markets and sell its existing products. Market development is often a natural progression from market penetration.
This is particularly attractive as an option to achieve economies of scale of production by widening the market. Firms also use this strategy to access new markets located in different geographies.
Once a business starts maturing after having captured much of the market share, it starts experiencing slower growth in the existing market.
That is why it is important to start looking at new markets where the business can expand, before it starts hitting a plateau in its existing market. This approach will help the business survive difficult times and will also gain an edge over its competition.
Market development is achieved by promoting existing products or services to a new audience through carefully segmenting, targeting and positioning the product or service.
This may involve new geographical markets, new segments, new or different distribution methods to get to new markets eg: pop up stores or vending machines and overseas market expansion into new countries and markets.
Diversification
In this strategy, a company creates new products which it sells to new markets. Developing new products for new markets is known as diversification.
This strategy can help a business to survive difficult economic periods or focus their brand in a different direction. Sometimes this involves forming a strategic alliance or joint venture with another business to create a separate range of products or brand.
The diversification strategy is conisdered to be the riskiest (and most challenging) of all the other growth strategies because the firm is trying to sell a new product (so there is uncertainty about its acceptance) and that too in a new market (where it may not have deeper insights about the market).
This strategy is usually undertaken only when a firm has a good understanding of its target industry and target audience, or has a brand that can adapt and leverage its market power to new (often) unrelated markets.
Popular example of the diversification strategy is Richard Branson’s Virgin, which operates in different markets and caters to different customer types eg: Virgin Transatlantic, Virgin Media, Virgin Mobile, Virgin Money.
How Firms Use These Strategies
Firms try to achieve substantial growth using various strategies such as Development of innovative technologies/ use of social media/ digital platforms. Investment marketing activities to increase awareness or deeper penetration into the market.
New product or service innovations. Overseas market growth. Improving supply chain management efficiencies. Outsourcing of activities to improve cost efficiencies, Evaluation of suitable joint venture partners etc.
Firms may use growth strategies which are a combination of some of the: Market penetration of existing markets. New Product or service Innovations. Market Development/ International Market Development.
Diversification into other sectors & products (possibly related to existing business). Firms achieve these through one or a combination of: Organic growth within the business, Joint Ventures/ alliances where it gets into acquisitions/ mergers with other firms.
Each strategy has a clear strategic rationale linked to some specific strategic objectives of the company. These strategies link back to the earlier analysis (PEST/ SWOT/ 5 FORCES etc.) that the firm may have done as part of its strategic analysis.
References
Ansoff, H.I., 1965. Corporate strategy: An analytic approach to business policy for growth and expansion. McGraw-Hill Companies.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.