Understand the annual report and its key components and why they are more just numbers. Here’s your ultimate guide to company performance metrics. Learn to interpret and analyse the Income Statement and Statement of Financial Position.
What is the Annual Report?
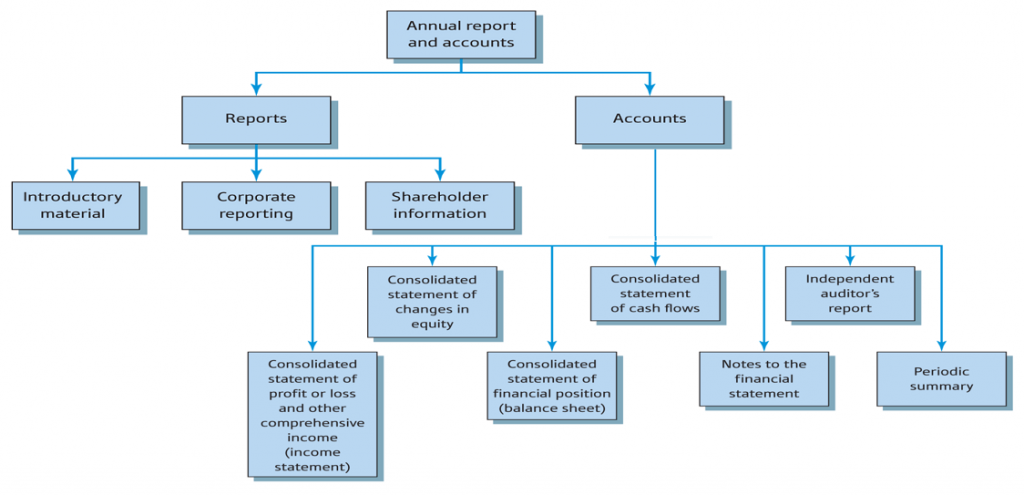
The annual report is a comprehensive report that provides information on the financial performance and operations throughout of a company for the preceding year.The annual report of a company includes the Income Statement, Statement of Financial Position (also known as a Balance Sheet) and other financial statements such as a Cash Flow Statement and a Statement of Changes in Equity.
It also included other useful information such as management discussion and analysis of financial results, it includes description of the company’s business operations, and also provides details about any significant events or transactions that occurred during the year.
In general, the annual report is produced once a year.
Objective of the Annual Report
The annual report helps investors and other stakeholders understand and evaluate the financial health of a company.
These statements provide important information about a company’s profitability, financial health, and ability to generate cash flow, helping investors and stakeholders make informed decisions about their investments.
Production of the annual report and accounts is required by law in most countries. The objective is to provide information useful to decision makers within key stakeholders including shareholders, governments, commercial banks and employees.
Content of the Annual Report
In addition to the financial results, the report also includes management discussion and analysis of financial results.
Key elements of the report that one should read are: The chairman’s statement; The financial summary; and the Accounts.
- The chairman’s statement is a brief written account of the major developments for the year.
- The financial summary describes performance against plan.
- The accounts contain the financial statements.
The Income Statement
Abbreviated to “income statement”, the formal full name of this statement is the Consolidated statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income.
The statement details the income less the expenses of an organisation over a period of time, usually one year.
Income – expenses = profit.
Profit is one of the most common measures of business success and is often one of the main performance criteria for setting management compensation.
Profit is subjective
It is important that you appreciate that accounting number are both an estimate, and are also subjective.
In a simple small business there is no controversy. For example Jim buys $50 of fruit and vegetables in the morning and sells them for $70. The Profit is thus $20.
In practice, for large businesses it is far more complex, profit is subjective. Accounting concepts have to be employed including dealing with:
- a. Matching concept
- b. Estimation
- c. Changing prices
- d. Wearing out of assets
Statement of Financial Position
Often called the “Balance Sheet”, the Statement of Financial Position focuses on assets, liabilities and equity at the year end. This statement provides a snapshot of a business at a particular point of time.
Assets – Liabilities = Equity
Assets are items that are owned or leased. Liabilities are amounts owed. Equity shows the claim of the owner.
Main Components of Statement of financial position
- Non-current assets: Used to run business long-term, eg. Equipment and buildings
- Current Assets: Short-term assets like stock (inventories) and debtors (Accounts Receivable)
- Current Liabilities: Amounts falling due within one year like creditors (Accounts Payable)
- Non-current liabilities: Amounts falling due after more than one year, like borrowings.
- Equity: Amount business ‘owes’ to owners.
- Profit: Income less expenses accumulated over the years.
- Drawings: Funds taken out of the business by the owners.
Related: Best Finance and Accounting books
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.