
Understand the purpose of budgets, learn to interpret information provided in budgets, and learn to critique the benefits and shortcomings of budgets.
Why is Budgeting Important
So what is the purpose of budgets?
We all budget in our personal life, such as for holidays or making a bigger purchase. Businesses also do the same.
A budget is a future plan which sets out a business’s financial targets, and helps turn long-term strategic objectives into reality.
“A budget is a future plan which sets out a business’s financial targets”. (chartered Institute of Management).
Compared to other financial reports (which are backward looking), a budget is forward looking.
Main benefits of budgeting to the business
- Promote forward thinking and identification of short-term problems
- Motivate managers to better performance
- Provide a basis for a system of control
- Help co-ordinate the various sections of the business
- Provide a system of authorisation
All business regardless of size produce a cash budget. Banks will often insist on it before lending. It starts with opening cash balance and shows cash movements in the period to give a closing cash balance.
Key Aspects of Budgeting
The key aspects of budgeting include Planning, Coordinating, Control, Providing Motivation, and Providing a system of authorisation. It is important that mangers must clearly understand the budget setting process.
The budget setting process typically involves a series of steps to create a financial plan for the firm.
It involves deciding the overall financial goals, scope and duration of the plan. It requires gathering relevant data, and estimating anticipated revenues and expenses for the period of the budget plan.
The control process, on the other hand, involves monitoring performance against the plan, identifying variances, and taking corrective action to address any issues that arise.
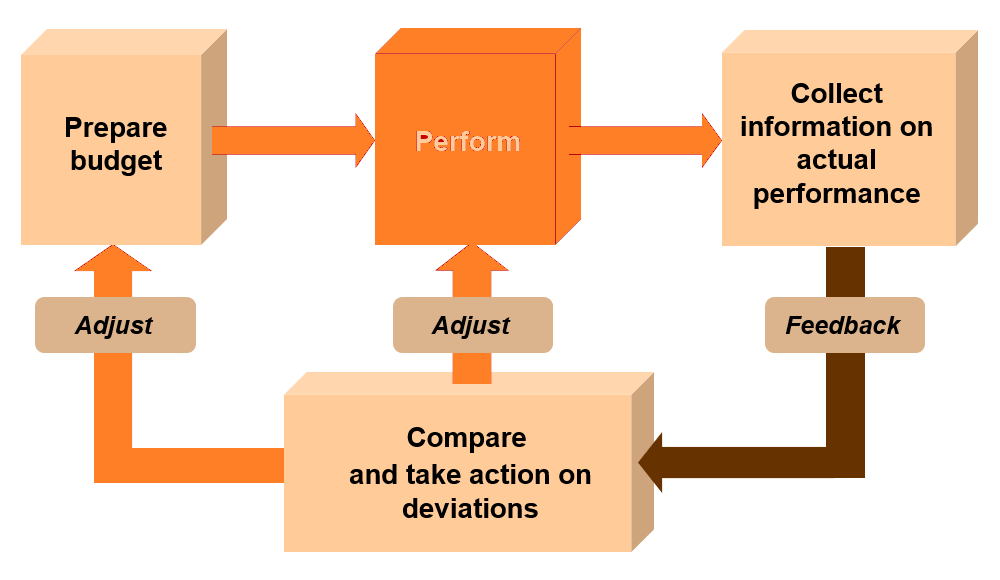
Planning and control process
- Establish mission, vision and objectives
- Undertake a position analysis
- Identify and assess strategic options
- Select strategic options and formulate long-term (strategic) plans
- Prepare budgets
- Perform and collect information on actual performance
- Identify variances between planned (budgeted) and actual performance
- Respond to variances and exercise control
- Revise plans (and budgets) if necessary
Budgetary Control Process
The Budgetary Control Process is about systematically monitoring and managing financial performance. It involves comparing the actual financial results with the figures that were budgeted figures. It is basically the relationship between the budgeted and actual profit.
Variances measure the difference between the budgeted/planned figures and the actual figures. Variances can occur in revenue, expenses, sales volume, or any other financial metric that was budgeted.
Budgeted profit + All favourable variances – All adverse variances = Actual Profit
Managers must monitor performance against budget, usually using variance analysis. The frequency of this usually increases with business complexity. Necessary action must be taken to rectify problems.
Sales volume variances: Difference between profit shown in original budget and profit shown in fixed budget
Sales price variances: Difference between actual sales and sales shown in the flexed budget
Materials variances, an example of cost budgets.
- Total direct material variance: Difference between actual direct materialcost and direct material cost as per the flexed budget (budgeted usage for the actual output)
- Direct material usage variance: Difference between actual amount of direct materials used and amount as per flexed budget (budgeted usage for actual output). Multiplied by the budgeted direct material cost per unit
- Direct material price variance: Difference between actual cost of the direct material used and direct material cost allowed (actual quantity of material used at the budgeted direct material cost)
Budgetary control can be made effective by focusing on the the following:
- Have a clear demarcation between areas of managerial responsibility
- Make budget targets that are challenging yet achievable
- Adopt established data collection, analysis and reporting routines
- Generate reports that are aimed at individual managers
- Have fairly short reporting periods
- Generate timely variance reports
- Ensure seriousness about the system
- Take action to get operations back under control
Criticisms of conventional budgeting
Budgets that are fixed may not be adequate measures of reality. Circumstances might change, which means flexibility is needed in the budget to reflect this. The old production economy was more suited to budgeting compared to the new information technology economy.
Most common flexibility is needed at activity level. For example in production or sales (“Activity-based budgeting”).
Despite its benefits, there are some criticisms of conventional budgeting such as being inflexible towards changes in the business environment.
Here are some more criticisms:
- Cannot deal with fast-changing environment
- Focuses on short-term targets
- Reinforces ‘command and control’ structure
- Very time-consuming and costly
- Too much linked to traditional functional areas
- Encourages incremental thinking
- Tends to protect costs rather than lower them
- Promotes managerial sharp practice
In recent years, alternative budgeting methods such as Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) and Beyond Budgeting have become popular, due to criticisms of traditional budgeting.
Zero-based budgeting (ZBB)
ZBB encourages a more questioning approach. However, it may be costly to implement, and may make employees feel threatened.
Behavioural issues of budgetary control
The effectiveness of the budgeting process can be impacted due to behavioral issues such as psychological and social factors, which can result in inaccurate budgets, reduced accountability, and even demotivation.
Dysfunctional behaviors of managers, budgetary slack, lack of motivation or participation from employees, are some behavioral issues.
Some managers may be motivated to meet short-term goals without worrying about its long-term performance on the company. They could engage in budgetary slack which involves deliberately setting much lower budgets.
Some employees may feel they have no input or ownership in the budgeting process which could hamper the effectiveness of the budgeting process.
Management must take these issues into account and incentivize behaviors that are in line with the long-term goals of the firm.
- Budgets can improve job satisfaction and performance
- Demanding, yet achievable, budget targets can motivate more than less demanding ones
- Unrealistically demanding targets can adversely effect managers’ performance
- Participation of managers in setting their targets can improve motivation and performance
Understanding the behavioral elements related to budgeting is important for firms improve their budgeting processes and to achieve their financial goals more effectively.
Budgeting and budgetary control systems behavioural elements include Consultation with various teams, Education & training, Independence and free from biases, Non-disciplinary, Involvement and proper implementation.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.