Stability of the Market Economy Classical/Neoclassical View The economy is inherently stable. Any instability is a temporary phenomenon as the market (forces of demand and supply) has strong self-correcting tendencies which make it stable. For example, this is highlighted by: The market for loanable funds The important characteristics of this market are: The economy’s output […]
Economics
Goldilocks Economy Explained
A Goldilocks economy is an ideal economic state where every thing is economic stability. There is optimal growth, low inflation, full employment, balanced saving and spending. In such an economy, there is no risk of high inflation or recession. In the economic climate, there are three basic conditions: hot, cold and warm. A hot climate […]
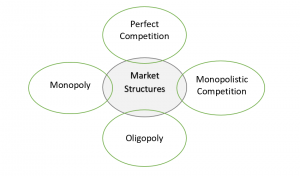
Types of Market Structures Explained
Market structure refers to how a market is setup, its organizational characteristics and the level of competition within the market. Market structure influences pricing, product differentiation, and other market dynamics. Perfect Competition In a perfect competition market structure, there are many buyers and sellers. There is no one big seller that dominates the market. Monopolistic […]
Measures of Economic Activity and Wellbeing
The learning outcomes for Economics are very broad and require us to take a critical perspective on economics. Thus, we cannot simply go through the typical introduction to economics topics such as the supply/demand model, perfect competition, monopoly, macroeconomic income determination and the like. We do go through each of these topics but we also […]