The customer loyalty ladder is a hierarchical model that enables businesses to classify customers based on their relationship and level of engagement with the business. It is a valuable tool to understand and nurture customer relationships that helps businesses increase customer satisfaction and create long-term loyalty.
Satisfaction and Loyalty
Satisfied customers provide positive word of mouth, buy a greater variety of products thereby increase profits and improve company value.
Satisfaction is an evaluation of total purchase and consumption experience of a good or service over time. Transaction-specific customer satisfaction, on the other-hand, is an immediate post-purchase evaluation.
Customer assessments of product or service performance depends on factors such as the type of loyalty relationship the customer has with the brand.
A customer-centred business may seek to create high customer satisfaction although that is not its ultimate goal.
The company must deliver a high level of customer satisfaction subject to also delivering acceptable levels to other stakeholders, given its total resources.
Satisfaction also depends on product and service quality.
Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs. Product and service quality, customer satisfaction, and company profitability are intimately connected.
Satisfaction is the difference between Service Expectations and the actual Service level received. If services rendered exceed what was expected, the consumer is satisfied.
Bond Between Customer and Company
Satisfaction level is a metric used to measure the bond between the customer and the company.
There are three types of relationships that a company can have with its customers based only on satisfaction were viewed as the weakest.
- An acquaintance relationship exists when a customer is satisfied with the product or service a company provides because it is on par with what he or she could get elsewhere.
- A friendly relationship exists when the customer trusts that a company provides differentiated value.
- A partner relationship exists when the customer is committed to the company because it provides customized value.
Since satisfaction leads to loyalty and retention, it needs monitoring. Satisfaction is monitored by systematically measuring customer treatment, identifying the factors shaping satisfaction, and changing operations and marketing as a result.
Satisfaction Measurement Techniques: Periodic Surveys, Customer Loss Rate, Mystery Shapers
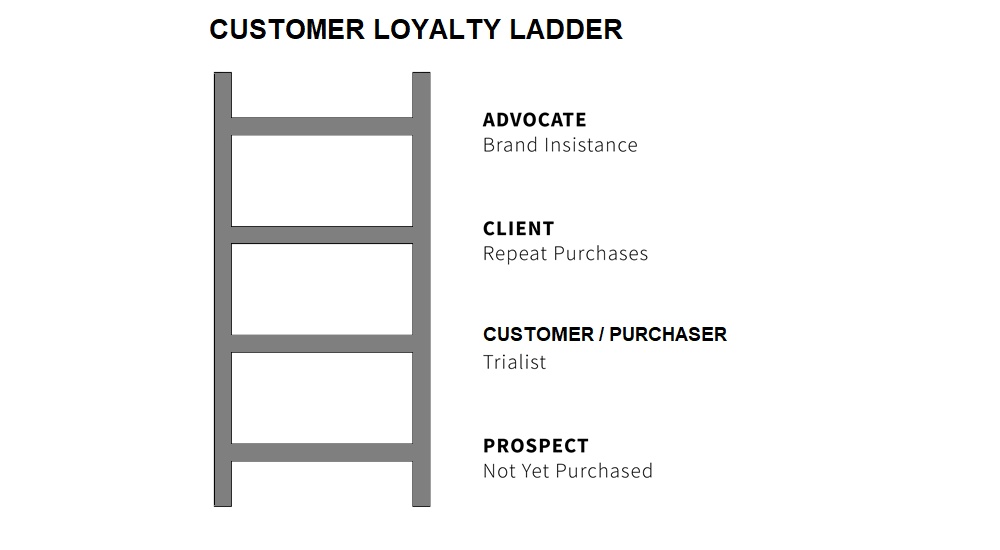
Understanding the Customer Loyalty Ladder
Loyal customers are high in repeat purchase behavior and strong in attitude are the most desirable customers. Loyalty indicates a commitment to the support of a relationship. Businesses need new customers, but they must also retain existing customers.
Loyalty has been defined as: “a deeply held commitment to rebuy or repatronize a preferred product or service in the future despite situational influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching behavior.” Kotler and Keller (2015).
A customer loyalty ladder helps a business understand how to nurture and incentivize customer relationship to keep the customer loyal. It enables businesses to develop effective strategies for engaging and rewarding customers as per their individual needs, which helps increase customer satisfaction and create long-term relationships.
Benefits of the Loyalty Ladder
Better Customer Insights: Monitoring customers’ progress through the loyalty ladder provides valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs, which can help a business improve its customer support, products and services.
Cost-Effective Marketing: Understanding the loyalty ladder enables businesses to allocate their marketing resources more effectively, In general, the more loyal customers are typically more receptive to upselling and cross-selling opportunities, making marketing ROI higher for such customers.
Enhanced Brand Reputation: Customers at the top of the loyalty ladder often become advocates for the brand, sharing their positive experiences with others and enhancing the brand’s reputation.
Various Stages of Loyalty Ladder
The ladder of loyalty typically breaks down into several stages, each representing a different level of commitment and engagement from the customer.
Suspect: Someone that fits within the target market but may not be aware of the business or its offerings. At this stage, there is no relationship.
Prospect: Someone who has shown interest in the business by making an inquiry or request. They are aware of the business and its offerings but have not made a purchase yet.
Purchaser: Someone who has done business just once with your organisation. It is important to encourage such consumers to repeat purchases and build a positive experience for them to move them up the ladder.
Client: Someone who has done business with you on a repeat basis due to positive experiences, but may be negative, or at best neutral, towards your organisation.
Supporter: Someone who likes your organisation but only supports you passively. It involves engagement and community building, indicating a higher level of commitment for the business.
Advocate: Someone who actively recommends you to others, who does your marketing for you. They are placed towards the top of the ladder, and are valuable assets who should be nurtured through loyalty rewards, invites to promotional events, and excellent customer service.
Partner: Someone who has the relationship of a partner with you. This stage likely represents the highest level of engagement and collaboration between the customer and the business, indicating a mutually beneficial relationship.
Related: More CRM concepts
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.