Economic integration is an arrangement between several countries to improve trade between them.
In the global landscape, Economic Integration usually can be classified into various additive levels.
Regional Economic Integration (Preferential Trade Agreement)
The WTO promotes free trade on a global basis, however countries in each of the world’s regions are seeking to liberalize trade within their own regions.
Preferential trade agreement (PTA) is a mechanism that confers special treatment on select trading partners. These agreements must be proved and accepted by the WTO.
PTAs unfold as one of the below mentioned forms/levels of economic integrations.
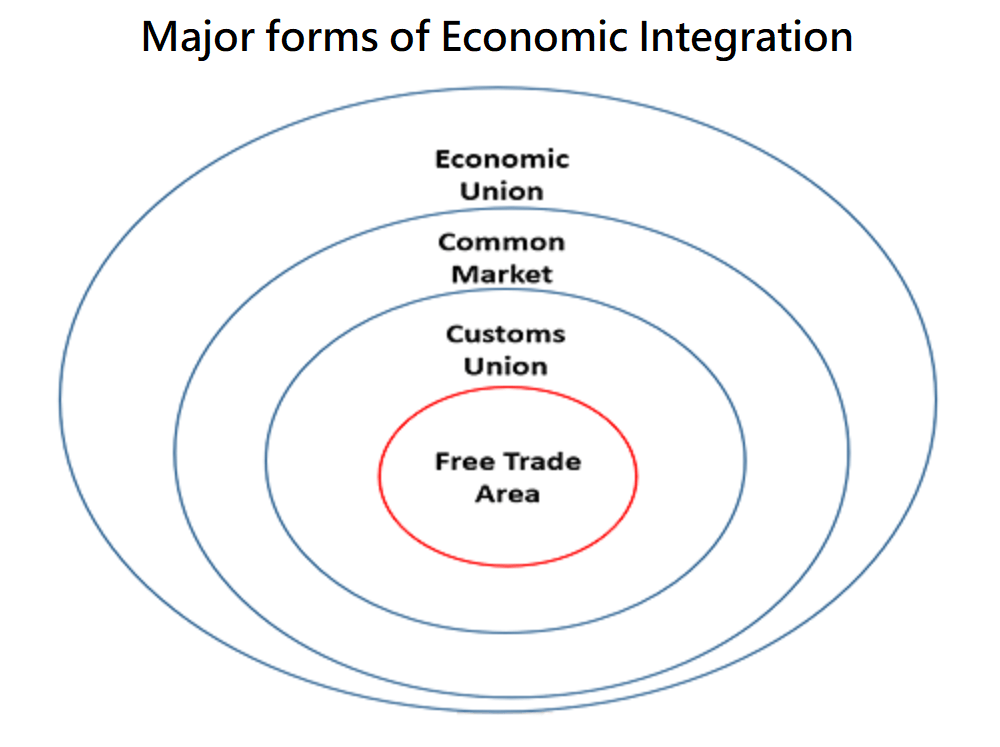
The figure summarizes the major forms of economic integration in regional markets and shows the varying degrees of formality with which integration can take place.
Free Trade Area (FTA)
FTA is the least restrictive and loosest form of economic integration among nations. All barriers to trade among member countries are removed. Each member country maintains its own trade barriers towards non-members. Overall around 50% of the global trade takes place among nations linked to FTA’s.
Examples
- European Economic Area, a free trade area that includes the 28 EU nations plus Norway, Liechtenstein and Iceland
- The Group of Three (G-3) encompassing Colombia, Mexico, Venezuela
- North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) including The United States, Canada, Mexico
Customs Union
A customs union represents the logical evolution of an FTA. As in the free trade area, goods and services are feely traded among members of the customs union, however, in addition the customs union establishes a common trade policy with respect to non-members. Typically this takes the form of a common external tariff.
Examples: Andean community, SICA, Mercosur, CARICOM
Common Market
A common market is the next level of economic integration. In addition to the removal of internal barriers to trade and the establishment of common external tariffs, the common market allows for free movement of factors of production, including, labour and capital.
Example: East African Community
- Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda, South Sudan and Burundi are the nations that make up the world’s newest common market
- The formation of the common market in 2010 resulted in free movement of people, goods and services and capital within the community
- Members also intend to move swiftly to establish a economic union
- The first step towards that will be creating a monetary union (a common currency)
Economic Union
An economic union builds upon the elimination of internal trade barriers, the establishment of common external barriers, the free flow of factors.
In addition, it seeks to coordinate and harmonize economic and social policies within the union to facilitate free flow of labour, capital, goods and services from country to country.
It involves the creation of a unified central bank; the use of a single currency; common policies on agriculture; social services; welfare; regional development, transport; taxation, competition, and mergers.
The EU is approaching its target of completing most of the steps required to become a full economic union.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.