The Internal Environment includes all aspects that are directly within the span of control of the global company and can be altered, stopped or started at its decision, e.g. strategy, structure, people, processes, resources.
What is the Internal Environment?
The internal environment refers to the culture, people (directly or indirectly related to the organization), events and factors within an organization that can influence the working of an organization.
The internal environment of an organization can be controlled, whereas a firm cannot influence the external environment.
Advantages of Internal Analysis
Analysing the internal environment enables a business to understand its areas of strengths and areas with problems. This helps the business to formulate appropriate strategies and increases the chances of success.
Here’s how Analysis of Internal Environment helps:
- Identify strategic capabilities in terms of organisational resources & competences & how these relate to the strategies of organisations
- Analyse how strategic capabilities might provide sustainable competitive advantage on the basis of their
- Value, Rarity, Inimitability & Organisational support (VRIO)
- Diagnose strategic capability by means of VRIO analysis, value chain analysis, & SWOT analysis
- Understand how to manage & develop strategic capabilities
What to Analyse in Internal Environment?
In Johnson’s Exploring Strategy Model, under Strategic Position, one finds ‘Resources’ which is what one analyses as part of Internal analysis.
Here’s what is typically analysed in the Internal Environment:
- Organisational resources and capabilities such as: core competencies, human resources, financial resources, informational resources, supply resources.
- Current offerings such as: product and services being offered, product mix and lines, sales, features and benefits, pricing and profitability, contribution to performance.
- Previous performance such as: previous year figures on sales, profits and financial results, historic trends in sales and profits, results of earlier marketing plans, customer relationship trends and costs.
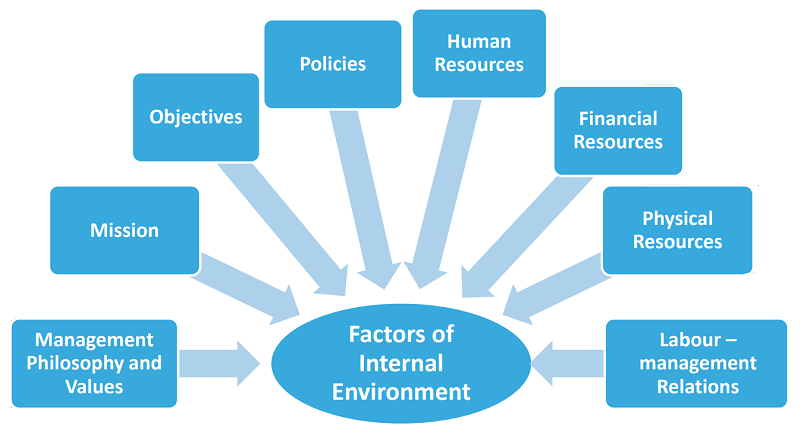
The various internal factors that can influence business strategy and other decisions include: Management Philosophy and Value system: This includes culture, work processes, norms and management practices of the organization. Vision, mission and objectives. Organisational Structure. Organisational Policies. Corporate Culture. Human Resources. Marketing. Management. Financial Resources. Physical Resources and Technological Capabilities. Labour Management Relations.
Strategic Capabilities: The Key Issues
Strategic capabilities refer to the resources and competences of a firm that it uses to compete with rivals in the market. These usually comprise a firm’s strengths and weaknesses and could serve as a source of competitive advantage (or disadvantage) for the firm.
Resources are Assets that a firm has. This includes:
- Physical: Machines, buildings, raw materials, products, patents, databases, computer systems
- Financial: Balance sheet, cash flow, suppliers of funds
- Human: Managers, employees, partners, suppliers, customers
Competences: what a firm does well. For example:
- Physical: Ways of achieving utilisation of plant, efficiency, productivity, flexibility, marketing
- Financial: Ability to raise funds and manage cash flows, debtors, creditors, etc.
- Human: How people gain and use experience, skills, knowledge, build relationships, motivate others and innovate.
Core Competences
A core competence is an activity or process that critically underpins competitive advantage & ability to add value. For example: what is done better, why these are done better, what secondary processes are done.
Examples of core competences: Expertise in integrating multiple technologies, Know-how in creating operating systems, Speeding new/next-generation products to market, Better after-sale service capability, Skills in manufacturing a high quality product, Capability to fill customer orders accurately & swiftly.
Capabilities: Adequacy & suitability of resources & competences to enable the organization to survive & prosper.
Strategic Capabilities
A firm may have different kinds of Strategic Capabilities:
- Threshold capabilities are those needed for an organisation to meet the necessary requirements to compete and achieve parity with competitors. This is about qualifying to ‘compete today’.
- Distinctive capabilities are those that are required to achieve competitive advantage & are difficult to imitate. This is required to ‘win today’.
- Dynamic capabilities are the means by which an organisation has the ability to renew & recreate its strategic capabilities to meet the needs of changing environments. This is needed to ‘win tomorrow’.
- Redundant capabilities: Capabilities, however effective in the past, can become less relevant as industries evolve and change. Such ‘capabilities’ can become ‘rigidities’ that inhibit change and become a weakness.
Various Tools & Models for Internal Environment Analysis
Various tools used for Internal Environment Analysis:
Value Chain Analysis
Value Chain Analysis is a means of looking at the value chain / network to understand how value to a customer is created / developed.
VRIO Model
Barney’s VRIO Model is a means of assessing the sustainability of an organisation’s capabilities.
McKinsey 7S Framework
McKinsey’s 7S Framework evaluates seven key internal elements (strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff) within an organization to assess its overall effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis draws together an understanding of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities & threats an organisation faces.
Resource-based Strategy
The resource-based view (RBV) of strategy asserts that the competitive advantage & superior performance of an organisation are explained by the distinctiveness of its capabilities.
It is sometimes also called the ‘capabilities view’.
Holonic Enterprise (HE) Model
The Holonic Enterprise (HE) Model is a model that can help enhance Internet-enabled global manufacturing supply chain and workflow management to better adapt to changing environments.
Holonic Enterprise Model is a highly distributed control paradigm in which the organization structure is based on autonomous and cooperative entities called “holon”. “Holons” which are units that act as complete autonomous units and also as interdependent parts of a larger system.
Such a structure allows flexibility and adaptability and enables the organization to better to changing environments.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking is a means of understanding the relative performance of organisations.
Activity Mapping
Activity Mapping is a means of identifying more detailed activities which underpin strategic capabilities
Read more on Strategic Analysis and Formulation
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.