One of the main objectives of the branding team of a company is to increase the brand equity of the organization. There are several ways in which this can be done, and one of the ways is to follow the Keller’s Brand equity model (also known as the CBBE model of Keller).
Introduction
Kevin Keller developed the Customer – Based Brand Equity (CBBE) model, which is a part of his popular textbook ‘Strategic Brand Management’.
As the name suggests, this model is customer based. Keller believes that Brand equity can be created by providing the right experience to your customer. The brand needs to shape up how the customers think and feel about the product.
Marketing and branding specialists need to manage the thoughts, feelings, beliefs; perceptions and opinions customers carry about a particular brand.
The higher the positive experiences created, higher will be the brand equity. A high brand equity results into brand loyalty and better brand sales.
The Models is also referred to as ‘Brand Resonance Model’ as it seeks to build a strong connection between the brand and the customer.
The model states that brands with high resonance have benefits like increased brand loyalty and reduced vulnerability to competitive marketing activity.
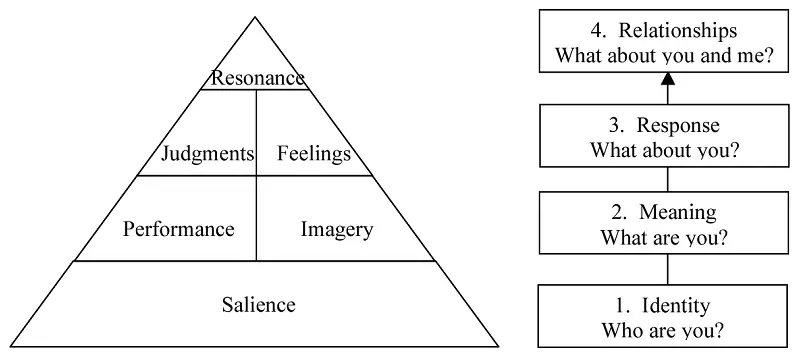
The model lists down four steps, which a brand needs to follow in order to build brand resonance and increase brand equity.
Read: What is Brand Equity?
Elements of Keller’s Brand Pyramid
The various steps of the Keller CBBE model include:
- Brand salience – how easily and often do customers think of a particular brand?
- Brand performance – how well do customers believe a particular brand performs?
- Brand imagery – describes the extrinsic properties of a brand (the colour, the packaging, the product consistency, associations) and level to which these satisfy customers’ psychological or social needs.
- Brand judgements – a customers’ own personal opinions and evaluations about a brand.
- Brand feelings – customers’ emotional responses and reactions with respect to the brand when prompted by communications or by friends.
- Brand resonance – the nature of the relationship customers have with the brand and the extent to which they feel loyal to the brand.
Step 1 – Brand Identity (Who are you?)
The key component at this stage is to develop a brand identity in the minds of the consumer. This stage aims at developing ‘Salience’ i.e. the customer needs to identify the product category the brand belongs to and have as fair idea of the needs it can satisfy.
To establish this, the main branding objective would be to develop a deep and broad awareness of the brand. The brand must be able to generate brand recognition and brand recall at the decision making time of consumers.
This stage involves creation of brand associations in the mind of the consumers’. These involve creation of brand name, logo, colour associates, mascot if any, tagline, brand symbol, etc. The concepts of STPD, i.e. Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning and Differentiation can be applied at this stage of marketing.
Step 2 – Brand Meaning (What are you?)
This stage aims at establishing a brand meaning for the consumer. The consumers must be able to understand what your brand means and what it stands for.
The main building blocks at this step are ‘Performance’ and ‘Imagery’. To achieve this, the branding objective is to create point of parity and difference.
Mere imagery is not sufficient; the brand also needs to deliver as per its promise in order to establish resonance with the customer.
Brand Imagery – It refers to the intangible aspects of a brand. It mainly deals with the method in which a brand aims to satisfy the social and psychological needs of a consumer. It comprises of sub-components such as:
- User profiles – means the type of people and organisations using the brand. It involves the demographic and psychographic segmentation.
- Purchase and usage situation – refers to the time and place when the brand is purchase, where it is purchased and if it is used for regular, occasional, formal, informal situations, etc.
- Personality and values – brands like people possess values. Keller talks about several aspects of brand personality such as sincerity, excitement, competence, sophistication and ruggedness.
- History, heritage and experience – mainly talks about the history and heritage the brand carries over the years and the impact it has on the perceptions of consumers.
Brand Performance – It refers to the tangible aspects of the brands. It mainly concerns the functional needs satisfied by the brand. The most important component of brand equity is the ‘product’ itself and how it delivers.
Keller listed the following sub-components of brand performance:
- Primary characteristics and secondary features – refers to the satisfaction of the core benefits of the product, which is its primary characteristic and the provision of ancillary benefits as part of secondary feature. For e.g. when you check into a hotel, a clean and hygienic room is a primary feature, whereas a complementary tray of cookies and coffee is a secondary feature.
- Product reliability, serviceability and durability – reliability refers to the consistence in brand performance over a period of time. Durability would mean the economic life of a product and serviceability relates to how easily the easy of servicing, repairs and after sales service provided by the brand.
- Service effectiveness, efficiency and empathy – service effectiveness means the extent of satisfaction of customers after service provision, efficiency refers to responsiveness in terms of time, speed, etc. and empathy reflects the care of customers and the trust evoked by the brand.
- Style and design – reflect the aesthetic components of the brand and are the most tangible. The look, feel, smell, texture, shape, size, colour play an important role in the consumer decision making process.
- Price – is one of the most important aspects of performance. Consumers’ generally form perceptions and expectations of a product on the basis of the price it commands in the market. A right pricing strategy goes a long way is generating brand equity in the long run.
Step 3 – Brand Response (What about you? )
This stage depicts the consumers’ response towards the brand. Its main building blocks are ‘Judgements’ and ‘Feelings’. It explains how consumers think and feel about the brand.
The main objectives of branding at this stage are to generate positive accessible reactions. These reactions are from the consumers’ and reflect their views which arise from their ‘head’ or ‘heart’.
Brand Judgements: On basis of their personal opinion and experience as well as contact with the brand, consumers’ tend to make judgements relating to the brand. These mainly originate from the mind of the consumer, i.e. it is a thought about opinion of a customer.
- Brand Quality – Ultimately consumers form opinions on brands on the basis of the quality it delivers. The perception of value and satisfaction mainly arise from quality of the brand.
- Brand Credibility – It reflects the credibility of the company or the organisation behind the brand. It refers to the extent a brand is credible mainly on 3 dimensions – brand expertise which includes competence and innovations, brand trustworthiness that talks about the brand being sensitive to the needs of the customers and brand likability which refer to the brand being fun and worth the time and effort.
- Brand Consideration –It reflects if the brand is in the consideration set of consumers or not while making a purchase. The brand has to be relevant to the needs of the customers and thus be in their consideration when required. Brand consideration is directly related to the strong and positive brand associations the brand has been able to generate.
- Brand Superiority – mainly reflects the competitive advantage a brand has as compared to other brands in the same category. It determines the extent to which a brand is unique and distinct in the minds of the consumer. Again the positioning of a brand and brand associations go a long way in determining brand superiority
Brand Feelings: They are the consumers’ emotional reactions and responses to the brand. It reflects how the consumers feel about the brand from their ‘heart’. The consumers’ feelings could be mild, intense, negative or positive depending on the communication of the brand and resulting perceptions.
- Warmth – refers to the soothing feelings that a brand generates from a consumer. Consumers may feel warm hearted, sentimental or affectionate towards the brand.
- Fun – feelings are amusement, joyfulness, playfulness, cheerfulness and light heartedness which are directed towards the brand.
- Excitement – brands can generate a feeling of excitement among consumers along with the feeling of being sexy, cool and alive.
- Security – brands may help consumers get rid of their problems and thus generate a feeling of safety, protection, comfort and self-assurance.
- Social Approval – when the brand satisfies the social acceptance needs of a consumer, it reflects social approval. A brand purchased by a consumer may be acknowledged by others and may also become a symbol of his / her social status.
- Self Respect – is generated when a consumers’ feels better about their own self by usage of the brand. The brands may help boost their confidence, looks or even a sense of accomplishment.
Step 4 – Relationships (What about you and me?)
The final step of the model talks about the ultimate relationship between the customer and the brand. This measures the bonding of the brand with the customers and is a true reflection of consumers’ continuity with the brand and allied products.
‘Resonance’ reflects the nature of relationship that a consumer develops with a brand and whether the brand is in sync with the customers’ needs. The main branding objective at this stage is to establish a deep and permanent loyalty among customers.
Brand resonance is at ‘top of the pyramid’ and the ultimate aim of any brand. Brands like ‘Apple’, ‘Harley Davidson’ are considered to be extremely high on brand resonance.
Keller further breaks up brand resonance into the following four categories:
- Behavioural Loyalty –It measures the repeat purchases of customers and the share of category accounted to the brand. The higher the brand loyalty, higher is the profitability as loyal customers help in reducing marketing costs, are immune to price changes and are the brand ambassadors through their word of mouth campaigns.
- Attitudinal Attachment –The positive association one carries regarding the brand and its reflection on brand attitude by consumers’ is a powerful measure of attitudinal attachment. Consumers who love the brand or cannot part with the brand are considered as being attached to the brand in the true sense.
- Sense of Community – identification to a brand community is a social phenomenon, where consumers feel affiliated and connected to other people using the same brand. It could be a part of social or reference group, where many individuals buy the same brand to have a sense of community with their counter parts.
- Active Engagement – the strongest measure of brand loyalty is when the customers are willing to invest time, money and resources into the brand and which extends beyond purchase and consumption of the brand. In the true sense, the customers become brand ambassadors and brand evangelists.
Brand Relationships are reflected by 2 dimensions – ‘Activity’ and ‘Intensity.’
Behavioural loyalty and active engagement reflect the ‘Activity’ a consumer has with the brand. This activity can be in terms of usage or indirect interaction with the brand.
‘Intensity’ is measured by the attitudinal attachment and community sense with the brand concerned.
Read: Branding and brand related concepts.
References
Farjam, S. and Hongyi, X., 2015. Reviewing the concept of brand equity and evaluating consumer-based brand equity (CBBE) models. International Journal of Management Science and Business Administration, 1(8), pp.14-29.
Wang, H., Wei, Y. and Yu, C., 2008. Global brand equity model: combining customer‐based with product‐market outcome approaches. Journal of Product & Brand Management.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.