
Marketing mix includes the “set of marketing tools that a firm can use to pursue its marketing objectives in the target segment”.
Introduction to 4P’s and 7P’s Marketing Mix
Marketing mix refers to activities that a firm carries out to effectively promote its products/services. This is done by adjusting the four Ps of the marketing mix: Product or service, Price, Placement, and Promotion.
Marketing Mix 4P’s: Product, Price, Place (distribution), Promotion – foundation model in marketing. This is the Shortened simplified version by Eugene McCarthy and now more commonly used (McCarthy, 1960).
Marketing Mix 7P’s: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, Physical Evidence (Environment) – generally used in the service industries.
The 7Ps marketing model is an extension of the 4Ps. This model adds three more elements—People, Process, and Physical Evidence—to the marketing mix, and makes it more comprehensive, especially useful for service-based businesses.
These models provide businesses with a framework to come up with an effective marketing strategy.
By carefully considering these elements, a firm is able to better cater to consumers in its target segment, price the products appropriately keeping in mind the firms objectives, promote the products effectively to its target segments, and is able to use the right distribution methods so that the products are easily made available to the target users (Green and Keegan, 2020).
By planning the marketing mix, a firm is able to create a cohesive marketing strategy to better position its products or services for the target audience in order to drives sales.
Depending on the markets, a firm may use Standardization or Adaptation of the marketing mix.
Standardization refers to the use of similar marketing strategies across the various markets, whereas Adaptation involves modifying the marketing mix to better meet the needs of the local markets (Green and Keegan, 2020).
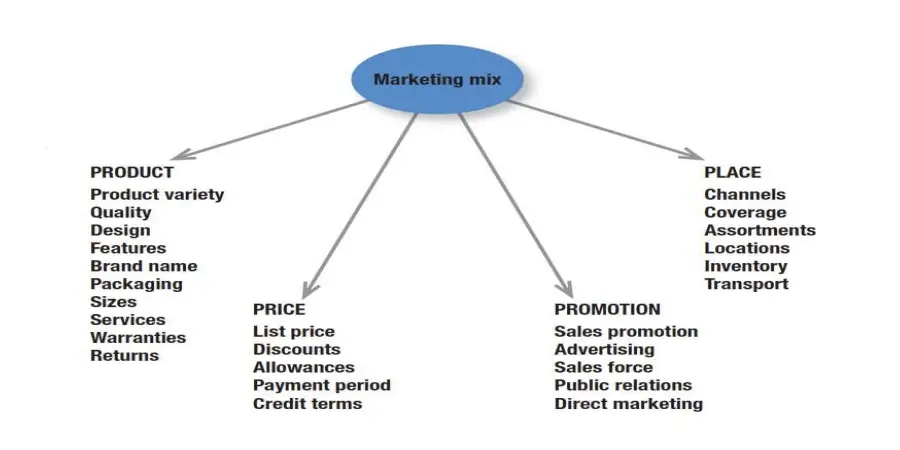
Products/Services:
Products / services is the P which gives an insight on how to develop one’s offerings.
Successful companies find out what customers/clients such as government agencies need or want and then develop the right product with the right level of quality to meet their expectations, both now and in the future. Effective design of product and services provides value for the customer.
- How are products and services designed and developed in your workplace in response to customer requirements?
- How do your feedback systems gather evidence about the adequacy of the design of these products and services?
- How do you find out what your customer’s needs are now and whether they believe these will change in future?
For example, groceries is one of the most common commodities used in day to day life, such businesses face tough competition from it’s competitors. The products in this case are items such as food grains, oils, spices, condiments, sugar, soaps, washing powder etc which are a part of day to life. They need to actively focus on how their products are better in terms of their quality, nutritional value, suitability, variety, appearance, packaging quality & sizes, shelf life and availability vis-à-vis the other retailers.
Their website portal should effectively convey all the positives of their products & how these will readily to cater to needs of the household and how the customer will stand to gain by opting for their products.
The products should be able to create a clear liking & preference in the minds of the customers so that they become repeat & regular consumers.
Read: Product Strategy & Value Proposition
Price
The money that a supplier charges for his product is labelled as price. Setting the price requires deep thought and analysis, as it needs to take into consideration not only affordability & profitability but also tough competition. This P is about arriving at an appropriate price.
A product or service is only worth what the customer is prepared to pay for it, so the price needs to be competitive, but this doesn’t mean you have to be the cheapest in your market.
Pricing is the key element of the marketing mix that generates revenue. For example government procurement is not sensitive to price alone, quality matters too.
- When tendering for business, how are decisions are made about price?
- What data is gathered to inform that decision-making process?
- How are the decisions about price on previous tenders monitored and reviewed?
A company, being faced by tough competition from various online stores, has no choice but to settle for low prices which will be attractive to the customers amongst the existing suppliers. The company may consider ideas such as discounts on quantity, freebies, slightly more quantities in the packages for the same price, direct / indirect savings, cashback, free delivery etc. The company also needs to be continuously vigilant about the prevalent market prices.
All said & done, one thing is certain, that in such a market environment the company has to content with wafer thin margins to survive and rather focus on expanding sales volumes (Top line) to build business & profitability.
Read: Pricing in the Marketing Mix
Place
The third P namely place is about geographies, locations & spots where the products or services are being sold or offered for a customer to avail; it also includes how the products are distributed & made to reach the customer in case of home delivery or online purchases.
This P is used in B2C commerce to ensure that a product/service is available in the right place, at the right time and in the right quantity, while keeping storage, inventory and distribution costs to an acceptable level. The place where customers buy a product, and the means of distributing the product to that place, must be appropriate and convenient for the customer. This is also applicable in some senses to B2G business. Some government contracts have requirements related to scale, the capacity to deliver services to a large population or across a dispersed geographical area.
The growth of e-commerce has also transformed the meaning of P3 in all sectors of business, including B2G. Via the Internet, businesses and government agencies use web sites to exchange information and do business with each other (e-procurement processes).
An example of good practice here is the use of a virtual workplace in which a business and an agency coordinate the work on a contract by sharing a common site to coordinate online meetings, review plans, and manage progress.
- How relevant are issues of scalability and capacity to the contracts you deliver and how are these addressed in the workplace?
- What e-procurement processes are used in government sectors of relevance to your workplace
- How effectively does your workplace use the internet to enable effective communication with customers?
Most companies nowadays plan to target metro / major cities where users are highly aware and acclimatized to online shopping and many of them are expected to be open to order groceries online as it offers lot of convenience and saves previous time and the bother of the cumbersome market visits. Such companies need to ensure that their website is made well known to customers from these cities, is user friendly and pleasant to experience, accessible through all connected devices including mobile phones and operates smoothly with a basic connectivity. The whole process of order pacing right up to online billing must be flawless accepting multiple payment modes. The website should be backed by an efficient round the clock helpline service to assist the customer when required.
There should also be an online easy access & mechanism for dispute resolutions including easy return, exchange or refund, as applicable. The company may identify & think of covering even those delivery addresses in the deep interior localities & difficult to reach which may be not be getting covered by other online competitors’ stores.
Read: Distribution Channels
Promotion
Promotion is the way a company communicates what it does and what it can offer to customers. It includes branding, advertising, PR, corporate identity, social media outreach, case studies, network management and exhibitions.
- What techniques are currently used in your workplace to promote your products and services?
- How are potential customers identified?
- What techniques are used to promote two-way communication and create a dialogue with customers?
- How do you promote your values, products and services to internal audiences across the company and supply chain?
This aspect of 7Ps is about impactful communication & building awareness of target customers about the product, it’s availability, benefits & uses. Although the aim is to reach out to as many customers as possible and maximise the sales, yet the promotional communication has to be truthful, ethical and just so as to let the customers have the correct know how about the product & it’s features.
For example, an online store has to be made widely known to people across the target cities which can be done through promotional campaigns using effective media channels such as Press, TV, FM, FB, Google & even hoardings. It’s a bit difficult to spend on promotional expenses in this case, anticipating the extremely tight profit margins, yet it needs to be done in whatever volumes and proportions feasible.
The promotional events can be conducted at Malls & Shopping centers where the company executives can speak & interact with the people; promotional messages can be displayed at places such as Malls, shopping centers, market place, Railway stations, Bus stands & other public places receiving high footfall. The company should also find out how the competitors carry out their promotional campaigns & what works for them and accordingly fine tune it’s own strategy.
Event marketing can be an effective marketing strategy that enables a business to achieve its goals and objectives. Internal factors that could affect an event include things such as creativity, location of event etc. On the other hand, external factors that may affect an event could include things such as competition, weather on the day of the event, the situation of the economy at the time of the event etc. Once all internal and external factors that could affect an event have been thought of, the business can then put a plan in place for worse case scenarios.
People
Everyone who comes into contact with your customers will make an impression. The people who have interactions with customers at all stages of contract negotiation, delivery, review and potential renewal will have a profound effect. The reputation of your brand rests in the hands of your staff, both face-to-face and online. Positive interactions with customers may become even more important than price for customers over time.
- How are new customers and business opportunities researched in your workplace?
- How are tendering processes for new business managed in your workplace?
- How effectively are two-way communications managed with your customers during the stages of contract delivery and review?
- How are relationships with end-users managed?
- What steps are taken to maintain positive views of the brand on social media?
This element emphasizes the importance of customer service personnel, sometimes experts and often professionals that are interacting with the customer. How they interact with customers, and how satisfied customers are as a result of their experiences, is of strategic importance for the company.
People in the form of employees are the face of an organization. Customers make their opinion and image of the company & it’s offerings based upon the experience they have while interacting with the people manning the company, especially the frontline staff.
This P is about knowing the right kind of people to be employed by the company & their capabilities, attitude, behaviour and skill etc. In the case of this start-up, the employees expected to come in contact with the customers are mostly the delivery & service staff and those manning the helpline.
The Top leadership of the company & their background also has a significant impact on the image of the company. In this case it has to be ensured that the delivery & service staff is absolutely well behaved, pleasant, courteous & fully knowledgeable about the product & services being delivered. The call agents manning the helpline also need to have similar capabilities apart from being very good in customer communication as well as resolving customer queries & complaints.
Process
Government customers do not simply buy a product or service; they set key performance indicators and expect these to be monitored and reported on. This means that the process of delivering the product or service is crucial to customer satisfaction and contract compliance.
- How does your workplace design and sustain effective processes for service delivery?
- During delivery of a contract, how is data gathered and action taken in relation to KPIs, service quality and customer satisfaction?
- How is contract compliance monitored and action taken as required?
This element emphasizes the importance of the service delivery; when processes are standardized, it is easier to manage customer expectations.
The process in this case is the entire sequence of activities & events right from a customer logging on to the website, browsing through the various products, making the selection, placing the order, making payment, actual delivery and complaint resolution, if required. As mentioned before the website needs to be appealing & user friendly, readily accessible through all connected devices, accept multiple payment modes and should operate smoothly with a basic connectivity.
The business needs to be backed by an efficient round the clock helpline and simple access & mechanism for dispute resolutions including easy return, exchange or refund, as applicable. The process of physical delivery needs to be well managed so as to deliver the right items at the right address within the committed timescales. The company may even consider outsourcing physical delivery activity but will have to ensure a pleasing and a hassle-free experience for the customer.
Physical Evidence
This concerns the physical or online environment (sometimes referred to as the ‘servicescape’) in which products and services are delivered. The physical evidence demonstrated by an organisation must confirm the assumptions of the customer, in terms of professionalism and appropriateness. This is an aspect of brand marketing.
Physical evidence also covers how the business will demonstrate what it is providing to their customers. This may take the form of case studies, testimonials, videos or statements of customer experience, for example.
- How does your workplace create and manage its physical environment for product/service delivery?
- How does your workplace develop and communicate its brand identity?
- How does your workplace capture and present evidence of its achievements?
The final one of the 7Ps is all about “seeing is believing”. It is all that the customer physically sees to be able to believe what the company is promising and accordingly make or desist from making a purchase decision. How appealing the company offices, premises, websites and staff members etc appear to a potential customer is what inspires confidence in the mind of a potential customer.
This step emphasizes that the tangible components of services are strategically important.
The Proof of the pudding is in the eating.
Again, in this case, the company will have to focus on putting up an attractive, pleasing & user-friendly website, confident and rightly knowledgeable customer contact staff, courteous and truthful response, good quality & hygienic packaging, active – energetic, polite & smartly dressed delivery staff and finally the actual reality of company’s business as advertised.
Useful References
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.