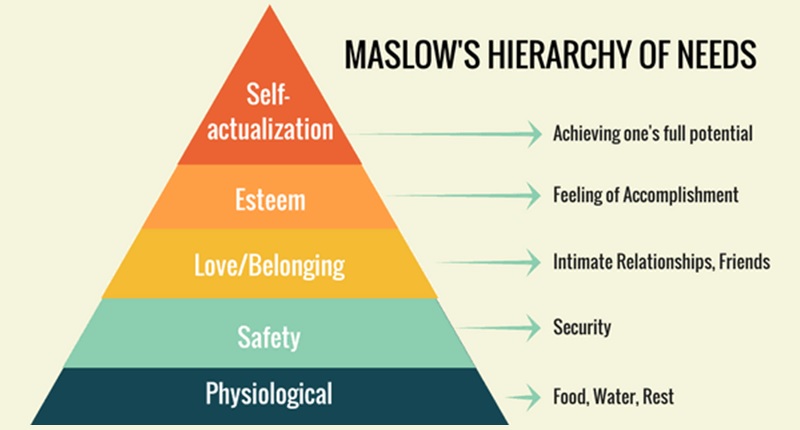
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory: Abraham Maslow propounded a theory of human motivation. Maslow identified five sets of human needs. The five sets of needs are arranged in a hierarchy of their importance to individuals.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs includes the following:
- Physiological needs
- Safety needs
- Social needs
- Esteem needs
- Self Actualisation needs
Highlights:
- Once satisfied, a need is longer a motivator
- Needs are satisfied in order
- If deprived of a source of satisfaction, a lower need becomes a motivator again
- Innate desire to work up the hierarchy
- Self-actualisation cannot be satisfied!
Physiological needs
These are the basic needs of human beings. It includes food, clothing, and shelter. Such needs lie at the lowest level of hierarchy. According to Maslow, such needs are to be satisfied first, and then the other needs.
Safety or security needs
These needs come in the second hierarchy of needs. Employees need:
- a. Job safety- so an organisation must adopt health and safety measures.
- b. Job security- so an organisation should provide permanent jobs.
Social needs
Human beings also feel the need to belong to a group or community. Nobody would prefer to live in isolation from rest of the society or group. They prefer to be loved and cared by others-i.e., their family members, work mates, friends, superiors, and others.
Esteem needs
It refers to ego needs.People want that others should respect them. People would also prefer praise and recognition from others. They want that others should have good opinion about them. It also includes ones feelings of self-worth and competence.
Self-actualisation needs
- These needs lie at the highest level of the hierarchy of needs. Very few people have such needs. Such needs induce a person to accomplish something special which others have not done.
- The need for challenging jobs, or the need for the highest level of promotion comes from these needs. In other words, through self-actualisation needs, a person feels the need to realise one’s potential to the highest possible level.
Features of Need Hierarchy Theory
Human beings have a variety of needs, not just a few, and they give varied importance to their needs, with some being more important than others. And that is what even the Maslow’s needs hierarchy suggests. Humans go after the basic needs first and once those are satisfied they start becoming aspirational. Also, once they achieve certain things, those things don’t motivate them any longer.
That’s what also capture by Maslow’s needs hierarchy.
All the lower level needs are placed at the bottom of the hierarchy, where as the more aspirational ones are placed at the higher levels.
Once the physiological needs such as food and shelter are taken care of, a human being pursues safety and security needs, and then they pursue social needs – the desire to be a part or a group, then they want people to respect them and acknowledge their work, and finally they reach the stage where they work towards realising their own potential.
- Wide range of needs: People have a wide range of needs. The employees put in their efforts to satisfy their needs. Human needs are multiple and inter-related.
- Structure of needs: Human needs are arranged into a hierarchy. There are some needs at the lower level, and there are some other needs at the higher level of the hierarchy.
- Lower level needs to be satisfied earlier: Lower level needs must be satisfied either wholly or partly before higher level needs emerge. In other words, a higher level needs does not become active, if lower level needs remain unfulfilled.
- A satisfied need is not a motivator: It is to be noted that a satisfied need is not a motivator. In other words, it ceases to influence human behaviour. It is the unsatisfied need that acts as a motivator.
- Inter-dependence of needs: A higher level need arises before a lower level need is completely satisfied. Thus, safety needs would emerge before the physiological needs are completely satisfied, and so on.
Need Hierarchy Theory: Pros & Cons (Advantages / Disadvantages)
Importance of Maslow’s Theory: Pros (Advantages)
The Maslow’s needs theory seem to take a logical approach because humans go after lower level needs first and then aim for higher things.
- This theory enables the managers to study human behaviour in different situations, and at different times. Accordingly, managers make an attempt to motivate employees by providing them monetary and non-monetary incentives.
- The analysis of physiological needs enables the managers to frame proper wage policies, so that adequate compensation or wages are paid to the employees.
- The study of security needs enables the managers to make the subordinates permanent by giving them job security. Also for adopting health and safety measures.
- The analysis of social needs enables the manager to make the employees members of quality circles, works committees or such other participative systems. The manager also invite suggestions from the subordinates.
- Ego needs facilitates promotions of employees, or the employees are given better status or designations. Deserving employees may be selected as leaders of certain work groups.
- A study of self-fulfillment needs enables the management to provide challenging jobs to dynamic and innovative employees.
Critical Appraisal: Cons (Disadvantages)
Maslow’s theory is criticised on the following grounds:
- All individuals need not have the same set of needs: It is often noticed that there are good number of individuals who are satisfied once their physiological and safety needs are fulfilled. Very few people strive to fulfil self-actualisation needs.
- Needs need not follow the pattern of hierarchy: There are cases where the needs need not follow the pattern of hierarchy as suggested by Maslow. There are cases of individuals who want to fulfill their self-actualisation needs even though their primary needs may not have been fulfilled. For instance, religious leaders may go on fast for days together to realise self-actualisation needs.
- Needs need not be the only determinant of behaviour: There are other motivating factors rather than needs alone. This includes experiences, expectations, perceptions, etc., that direct the behaviour of the individuals.
- Oversimplification of needs: Maslow has provided an oversimplification of human needs.
Maslow’s theory also has weaknesses and has been generally criticized due to the following reasons. First of all, not all humans are going to be motivated by the same set of needs (Reiss and Havercamp, 2005). In fact, there are many who may not be motivated beyond the first two or three levels; a lot of people are happy if their physiological and safety needs are met and they may not push themselves to fulfill the higher-level needs.
On the other hand, there are people who may want the higher level needs to be fulfilled even while they may not have fulfilled their primary needs first. The best example is that of religious leaders who may not care about the lower level needs but are very conscious about self-actualisation. Priorities are also going to change with age (Goebel and Brown, 1981).
So, needs of humans may not really follow the sequence mentioned in Maslow’s theory. Also, there are other motivating factors, besides the ones listed in this Maslow. Humans are also likely to be motivated by experiences, expectations, etc., that could motivate them to behave in certain manner (Berkowitz, 1967).
Application of Maslow theory
- An organisation can satisfy one level of need of employees, their motivations change as they aspire to reach the higher order needs.
- Within an organisation every employee is motivated to work through each of these levels. As they do so, this provides positive effects for each employee and the organisation.
Physiological Needs
An organisation offers competitive salaries. This gives people the means to acquire the basic needs for living. Flexible benefits programme allows employees to choose those benefits that suit them. This includes childcare vouchers, cash alternatives to company cars and discounted life insurance schemes. These savings and competitive salaries help workers’ pay go further and so motivate them to be loyal to the company.
Safety Needs
An organisation values the safety of all employees. The company is committed to providing a safe and healthy work environment to prevent accidents. Employees are however accountable- that means they have to take responsibility for observing the health and safety rules and practices. An organisation also offers employees a range of working patterns. Some may want to work part-time, others may want career breaks or undertake home working. This helps employees to choose the best option for a healthy work-life balance.
Social Needs
These are associated with a feeling of belonging. An organisation operates weekly group ‘huddles’. These provide informal opportunities for employees to receive and request information on any part of the business, including sales data and company products. This helps strengthen teams and enhances workers’ sense of belonging. Having an open approach to communication keeps everybody focused on the company’s aims helps individuals contribute to the company’s values. They include values such as being positive, seeing the best in people and recognising diversity. An organisation positively recognises and rewards staff achievements.
Self-Actualisation
An organisation provides employees with the opportunity to take on challenging and stimulating responsibilities. For example, the business provides the opportunity for individuals to take ownership of projects. This enables them to develop and improve.
Related: Theories of Motivation
References
Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review, 50(4), 370–396. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0054346
Goebel, B. and Brown, D., 1981. Age differences in motivation related to Maslow’s need hierarchy. Developmental Psychology, 17(6), pp.809-815.
Reiss, S. and Havercamp, S., 2005. Motivation in Developmental Context: A New Method for Studying Self-Actualization. Journal of Humanistic Psychology, 45(1), pp.41-53.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.