Omnichannel retailing is a business strategy of providing customers with a seamless experience by enabling them to interact with the brand using various channels, including offline as well as online channels.
Omni-channel retailing refers to the use of multiple channels to interact with customers and fulfill their orders. There is flow of Information, Products and Funds through these channels.
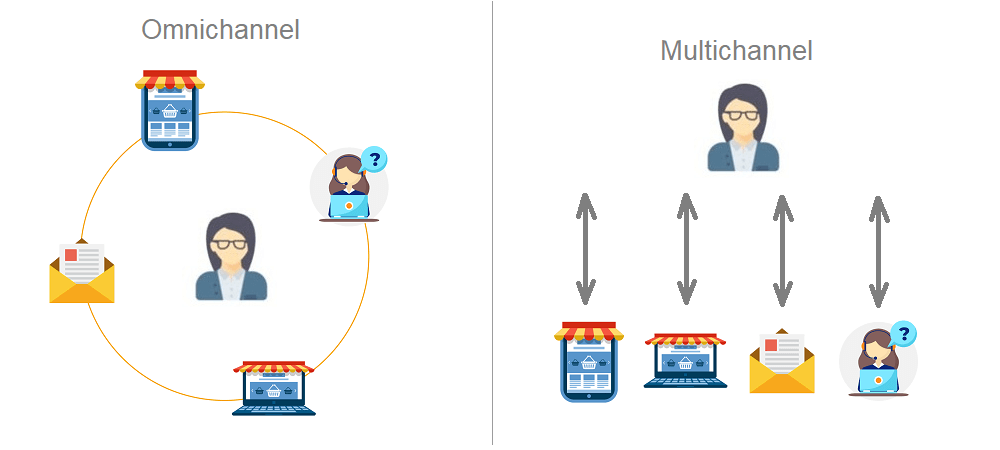
In omnichannel retailing, different channels of distribution are used with the focus being on customer whereas in multichannel retailing, different channels of distribution are used with the focus being on the product.
Traditional Retail
This channel involves face-to-face interaction where the Customer leaves with the product. This channel requires setting up facilities close to customers, maintaining high level of inventory, and there is low transportation costs.
Showrooms
This channel involves face-to-face interaction and the Product is ordered for later pickup. There is low level of inventory, smaller facilities. It requires more transportation and information infrastructure compared to traditional retail.
Online Information + Home Delivery
In this channel, there is aggregation of inventories. There are few locations and High transportation costs.
Online Information + Pickup
This channel reduces outbound transportation costs. The Customer must travel to pickup location.
Omni-channel retailing has the potential to combine the complementary strengths of physical stores and the online channel.
Factors such as product characteristics, customer needs, customer’s willingness to pay, influence choice of channels.
Product Demand Uncertainty and Omni-Channel Retailing
Here’s how Omni-Channel retailing reacts to Product Demand Uncertainty.
Predictable Demand Product
Traditional Retail compete on price, Showrooms are not suitable, Online Information + Home Delivery compete on service, Online Information + Pickup compete on ability to provide service at a lower price.
Unpredictable Demand Product
Traditional Retail compete on service for high information complexity products, Showrooms compete on price and variety for high information complexity products, Online Information + Home Delivery compete on price and variety, Online Information + Pickup compete more on price than home delivery option.
Product Value and Omni-Channel Retailing
Here’s how Omni-Channel retailing reacts to Product Value.
Low Value Product
Traditional Retail compete on price for predictable demand products, Showrooms compete on high variety at reasonable price for high information complexity Products, Online Information + Home Delivery compete on service, Online Information + Pickup compete on ability to provide service at a lower price.
High Value Product
Traditional Retail compete on service for products with uncertain demand and high information complexity, Showrooms compete on price for customizable, high information complexity products, Online Information + Home Delivery compete on price and variety, Online Information + Pickup become more competitive on price than home delivery option.
Product Information Complexity and Omni-Channel Retailing
Here’s how Omni-Channel retailing reacts to Product Information Complexity.
Low Information Complexity Product
Traditional Retail compete on price for predictable demand products, Showrooms are not suitable, Online Information + Home Delivery compete for uncertain demand products, Online Information + Pickup compete on price for uncertain demand products.
High Information Complexity Product
Traditional Retail compete on service for uncertain demand products, Showrooms compete on price for uncertain demand products, Online Information + Home Delivery compete on service in terms of variety and availability for uncertain demand products, Online Information + Pickup becomes a slightly cheaper option to compete on service in terms of variety and availability for uncertain demand products.
Performance of Channels: Customer Service & Cost
Here are some factors that has an influence on Customer service:
- Response time to customers: While online channel may be fastest for information goods, picking up physical products (from pickup centers or stores) may be faster than other channels.
- Product variety: It is easier to offer larger selection remotely
- Product availability: Aggregating inventory improves product availability
- Customer experience: The various channels have complementarity strengths
- Faster time to market: Online/showrooms are quicker compared to retailing
- Returnability: It is easier with physical locations. Also, proportion of returns are likely to be higher when information exchange happens remotely.
- Direct Sales to Customers: Manufacturers can use remote information exchange for direct access to customers
- Efficient Funds Transfer: Internet and smartphones
Here are the factors that has an influence on cost:
- Inventory levels: Businesses must maintain lower inventory levels if the customers are willing to wait.
- There are costs related to the operations of physical facilities in a network.
- Transportation costs are lower for information goods in digital form. For nondigital, aggregating inventories increases outbound transportation costs
- In general, higher investments are needed for channels that provide information remotely.
Effective Portfolio of Channels
Physical stores are good at letting customers experience high information complexity products in person. They are also cost effective at selling products with predictable demand. The online channel, in contrast, is cost effective at selling products with unpredictable demand but cannot let customers experience high information complexity products.
An effective portfolio results if brick-and mortar stores sell predictable demand items, serve as showrooms for high information complexity items with unpredictable demand, and serve as pickup locations for the online channel, while the online channel delivers unpredictable demand items to the customer.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.