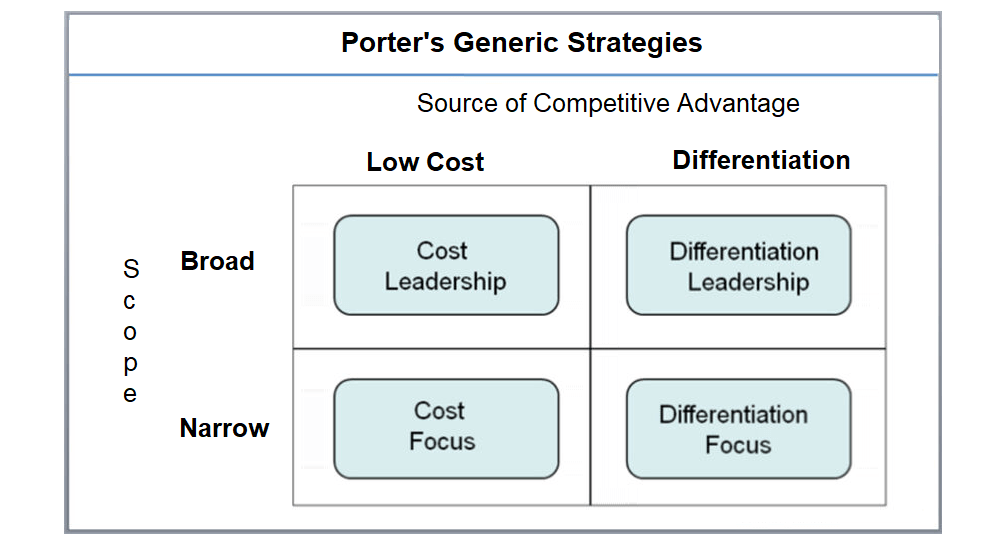
Porter’s generic strategies refers to strategies that companies can use to gain a competitive advantage in the market, such as Cost Leadership, Differentiation and Focus (Porter, 1985).
Every business wants to assess and understand competition so that they can plan their actions accordingly, and stay ahead of it. They want to know who the competitors are and how their actions could possibly impact their earnings and future planning.
An effective way to analyze competition is one of Porter’s Generic Strategies that provides more insight about the competition.
Michael Porter is an American academic known for his popular theories on economics, and business strategies.
Porter refers to the generic strategies as:
- Cost Leadership (no frills, keep cost down as much as possible). A company either chooses to lower the price of its products to beat the competitors.
- “Differentiation (creating unique products and services). A company might choose product differentiation based on the factors valued by customers to command a higher price.
- Focus (focus in a niche market). At times, a company may choose the “focus” strategy by concentrating on a small segment of the market to satisfy the segment’s unique needs or demand (also known as niche marketing). This part is further divided into two parts: “Cost Focus” and “Differentiation Focus.”
Basically, what Porter says is that a company’s business-level strategy should not involve trying to serve the varied needs of the marketplace at one go.
Instead, choosing to specialize or focus on certain aspects can be advantageous.
Implementing one of the generic strategies successfully gives advantage to an organisation in the market.
- Comparative Advantage: When a company has a comparative advantage, it is able to create products more efficiently than its competitors, which leads to better profit margins; because most buyers would naturally opt for cheaper products from all the options available.
- Differential Advantage: When a company builds differential advantage over the competitors, the company’s products or services are seen as of higher quality, which the company capitalizes on. It promotes the products saying that it is of superior quality, and may even charge a premium. Advanced technology, strong brand identity, patent-protected products or processes, usually offer differential advantage.
Cost Leadership
Achieve leadership in an industry by offering lower costs. No frills, keep cost down as much as possible.
There are several companies that create a competitive advantage for themselves by becoming low-cost sellers of products or services. This strategy provides numerous advantages to the company. Such companies focus on large volumes and thin margins but still earn better than their competitors.
Examples of companies that adopt this strategy include Wal-Mart, Costco, Nebraska Furniture Mart, Ikea (use this strategy in some countries such as India).
While being a low-cost buyer or seller can offer advantages, it’s not the only factor for success. Factors such as quality, customer service, brand reputation, and differentiation also play crucial roles in achieving sustained business growth and profitability.
Differentiation
Create unique products and services. Achieve leadership in an industry by offering differentiated products (people see the products as different from what others are offering).
There are several product as well as services companies that offer something distinct and innovative in their respective industries. Product companies such as Coca-Cola, Pepsi, Wrigley, Hershley, and services companies such as Moody’s Corp, American Express Co, Wells Fargo & Co, are some examples.[>
These are just a few examples of companies that have differentiated themselves by offering unique products and services in their respective markets. Uniqueness can come in various forms, including technological advancements, sustainable practices, design innovation, or disruptive business models.
Focus
Here, “Focus” means focussing in a niche market. This part is further divided into two parts: “Cost Focus” and “Differentiation Focus.”
Cost Focus: Focus on a narrow niche and offer lower costs.
Differentiation Focus: Focus on a narrow niche and offer differentiated products.
For example, and airlines may own a low-cost airline that offers no frills tickets, which are quite cheaper than what the competition offers. This strategy focusses on ‘cost leadership’. This strategy focuses on attracting volumes by offering reduced cost. On the other hand, some other airline may focus on on ‘product differentiation’, especially for their business and first class passengers. The airline will provide better services in the flight, will offer an expanded network across the world and so on.
Airlines may also adopt a ‘focused’ approach by focusing on certain routes, such as the Middle East, and try to offer a variety of great deals. It may tie-up with luxury hotel chains, offers different kinds of travel packages with adventures and offer other related product offerings within the hospitality industry.
These are Generic Strategies
Michael Porter refers to these approaches in his generic strategies.
These approaches are called “generic strategies” because they can be applied to products or services in any industries, and organization of any size. These strategies could be used by a company of any size (small, medium or big) to pursue its competitive advantage.
A lot of organizations nowadays adopt a mix of these strategies. There are many companies that follow a differentiation strategy wherein they offers quality products, but it offers a low price, because of which people see more value for their products.
Related: More theories, models and frameworks from Michael Porter
Recommended Books
Porter, M.E. (1985b). Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. New York: The Free Pess.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.