In Marketing, Positioning is a concept that outlines how a business should market its products/services to customers. In positioning, the marketing team creates an image for the product, for its intended audience.
The positioning process
Positioning is the act of designing the company’s offering and image so that they occupy a meaningful and distinct competitive position in the target customers’ minds. With positioning, you use marketing to create a competitively distinctive position for your product in the minds of targeted customers.
You need marketing research to understand how your targeted customers perceive your organisation, product or brand and your competitors. Research can also help to determine which attributes matter most to the targeted customers.
Regardless of how you see your products, it is the customer’s view that counts.
Two fundamental elements:
- Physical attributes – the functionality and capability that a brand offers.
- Communication – the way in which a brand is communicated and how consumers perceive the brand relative to other competing brands in the market place.
Applying Positioning
A marketing plan must should how you’ll actually carry through the positioning in your product’s marketing and performance.
- You need to determine whether your organisation can realistically develop and market a product that will live up to the meaningful points of difference you’ve chosen.
- Then consider whether the points of difference can be communicated to the targeted segments.
- Finally, be sure that you can sustain the product’s performance and differentiation over time.
Positioning (or repositioning) is the driver behind all the marketing activities you will include in your marketing plan.
With differentiated marketing, you develop a positioning appropriate to each segment and apply that positioning through your marketing decisions for each segment. With concentrated marketing, you establish one positioning for the single segment you target.
Remember that as markets evolve and customers’ needs change, you must be prepared to reposition a product, if necessary, for relevance, desirability, and deliverability.
Planning for Positioning
Use this checklist as you make decisions about positioning or repositioning your product or brand.
- What specific pants of differentiation are meaningful to your customers and applicable to your brand or product?
- How can you use differentiation to position your offer as competitively distinctive. desirable and superior?
- Is your positioning credible. relevant and realistic in the context of customers’ needs. your organisation’s capabilities and competing offers?
- How can you use your marketing mix to support, communicate and deliver on your positioning?
- If you choose differentiated marketing, how can you adapt your positioning for specific targeted segments or geographic markets?
- What changes in customers’ needs, competitive pressures or the marketing environment might cause you to undertake repositioning?
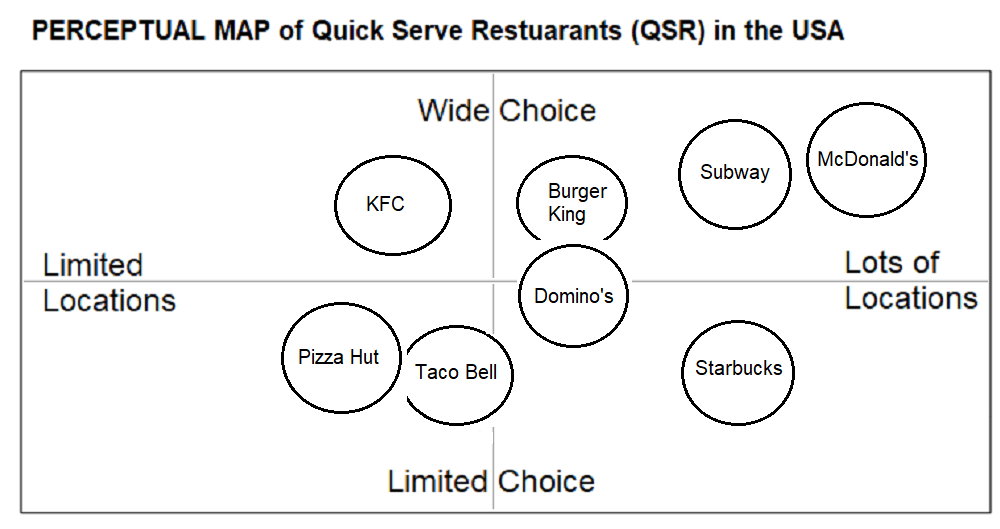
Positioning map
- What are the attributes that are important for customers?
- Research the competition
- Design a perceptual map and position the restaurant and its competitors
Defining associations:
- Points-of-difference (PODs): Attributes or benefits consumers strongly associate with a brand, positively evaluate and believe they could not find to the same extent with a competitive brand.
- Points-of-parity (POPs): Associations that are not necessarily unique to the brand but may be shared with other brands.
Repositioning Strategies
The following four ways outline how to approach repositioning a product, depending on the individual situation facing a brand. In some cases, a brand might need to be adapted before relaunch.- Change the tangible attributes and then communicate the new proposition to the same market.
- Change the way a product is communicated to the original market.
- Change the target market and deliver the same product.
- Change both the product (attributes) and the target market.
Related: STP process in Marketing
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.