Every new product goes through a product life cycle and the various stages in the life cycle impacts the marketing strategy and the marketing mix, and management decisions within the firm.
Before Porter’s famous Five Forces Model came into existence (in 1979), much of industry analysis was conducted on the basis of the product or industry life-cycle model.
Industry Life Cycle Analysis is part of fundamental analysis of a company involving the examination of the stage an industry is in at a given point in time.
The terms product life cycle and industry life cycle refers to the same thing – the various stages through which the product/industry goes through.
A product life cycle is the process (amount of time) a product goes through from getting introduced into the market until the time it is taken off the shelves.
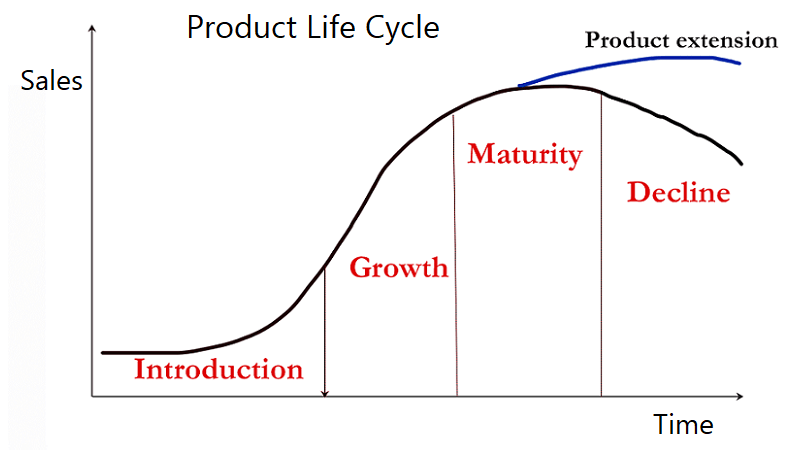
The product life cycle suggests that products and services will, over time, move through various stages: introduction, growth, maturity and decline, as shown in the diagram below. The lifecycle reminds us that products will only sell for a specific length of time and marketers must ensure that they are making the most of profitable stages in the cycle.
The product life cycle can apply to:
- a product class (computers)
- a product form (a laptop)
- A brand (Sony)
(Baines, Fill and Rosengren, 2017, p.314)
Product Lifecycle Stages
There are four stages in a product’s life cycle:- Introduction:
- Growth:
- Maturity:
- Decline:
Extending the product life cycle
The product life cycle can be extended:
- Introducing new ways of using the product
- Finding new users
- Developing new attributes
(Baines, Fill and Rosengren, 2017, p.314)
Embryonic / Start up
In the embryonic phase, mostly new companies were concerned with establishing a generic market for the product, to develop their technology, to be entrepreneurial and to establish the market as a stable one.
Growth
In this stage, the product bears fruit in terms of rapidly growing sales. Even then, profits would be small and the firm would need to reinvest to build capacity in order to meet the growing demand.
In this phase, successful company would be concerned to establish regular distribution, become the market leader and invest for the future.
Mature
As the industry approaches maturity, the industry life cycle curve becomes noticeably flatter, indicating slowing growth.
The same level of new investment would no longer be required, and the main aim would be not so much innovation as an increase in operating efficiency and productivity. This phase could be linked to the ‘cash cow’ phase of the Boston Box.
Some competition from late entrants will be apparent, and these new entrants will try to steal market share from existing products. Thus, the marketing effort must remain strong and must stress the unique features of the product or the firm to continue to differentiate a firm’s offerings from industry competitors.
Ageing
Ultimately, the ageing phase overtakes the market and the firm struggles to maximise cash. If product innovation has not kept pace with other competing products and/or service, or if new innovations or technological changes have caused the industry to become obsolete, sales suffer and the life cycle experiences a decline.
In this phase, sales are decreasing at an accelerating rate. Mergers and consolidations will also be the norm as firms try other strategies to continue to be competitive or grow through acquisition and/or diversification.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.