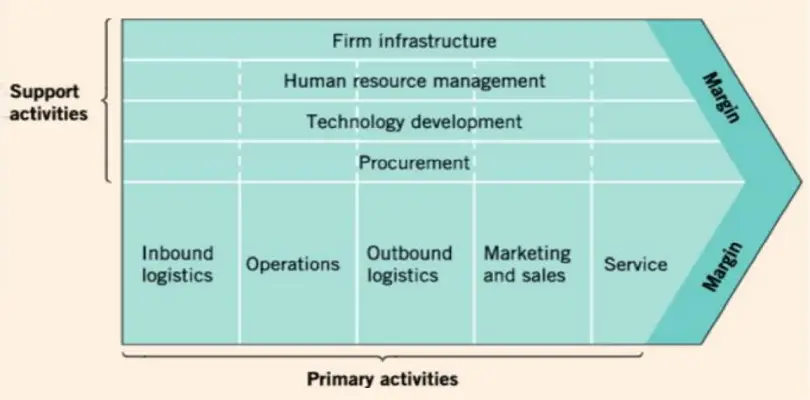
The value chain describes the categories of activities within an organisation which, together, create a product or service.
What is Value Chain?
Understanding how the company creates value, and looking for ways to add more value, are critical elements in developing a competitive strategy. Michael Porter discussed this in his influential 1985 book “Competitive Advantage,” in which he first introduced the concept of the value chain.
A value chain is a set of activities that an organization carries out to create value for its customers.
Porter proposed a general-purpose value chain that companies can use to examine all of their activities, and see how they are connected.
The way in which value chain activities are performed determines costs and affects profits, so this tool can help in understanding the sources of value for the organization. Competitive advantage can be analysed in any of these activities.
Rather than looking at departments or accounting cost types, Porter’s Value Chain focuses on systems, and how inputs are changed into the outputs purchased by consumers. Using this viewpoint, Porter described a chain of activities common to all businesses, and he divided them into primary and support activities.
For manufacturing companies, it involves activities such as procuring raw materials, the various manufacturing and marketing activities. It allows a company to easily analyse if the production can be made more efficient and it can provide more value at a lower cost.
Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics: Raw material handling, warehousing, receipt, stock control
- Operations: Machining, assembling, testing
- Outbound Logistics: Warehousing, distribution
- Marketing and Sale: advertising, pricing, promotion
Support Activities
- Procurement- refers to the function of purchasing inputs not to the purchased inputs themselves.
- Human resource management – management consists of activities involved in the recruiting, hiring, training, development, and compensation of all types of personnel; labour relations activities; and development of knowledge-based skills. Examples: recruitment, selection, training, reward polices
- Technology development- The activities, costs, and assets relating to product R&D, process design improvement, equipment design, computer software development.
- Firm infrastructure- systems, structures and routines
Part of the Internal Environment
The Value Chain is part of the internal environment of a business as it takes into account the various internal functions of an organization. The Value Chain model does consider the external environment in the sense that it recognizes that a business operates within a larger value system that includes its suppliers and customers, but primarily it focuses on the internal activities of the business.
Examples of Value Chain

Uses of Porter’s Value Chain
Uses of the value chain
- A generic description of activities – understanding how activities create value
- Identifying activities where the organisation has particular strengths or weaknesses
- Analysing the competitive position of the organisation using the VRIO criteria
- Looking for ways to enhance value or decrease cost in value activities
Issues with Value Chain
Downsides of Value Chain analysis
The Value Chain only tells us about what is happening within an organisation. It can ignore key issues. As a result, a wider approach is recommended.
Related: More theories, models and frameworks by Michael Porter
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.