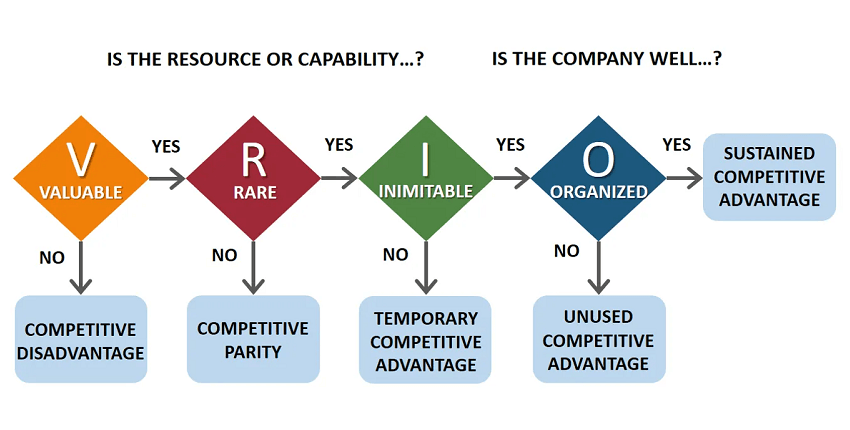
VRIO is am Internal analysis technique for doing Organizational Analysis. VRIO (acronym for value, rarity, imitability, and organization) framework helps understand the business elements that provides the business with a long-term competitive advantage.
VRIO framework analyses an organisations internal resources, processes, and capabilities to see how it could be improved.
Here is how VRIO is applied. Every capability is checked for the following:
- Is it Valuable?
- Is it Rare?
- Is it costly to imitate?
- Is the firm organized to capture value?
If yes to all, then the company gets Sustained / Long Term Competitive Advantage.
The VRIO Analysis was developed by Jay B. Barney as a way of evaluating the resources of an organization (company’s micro-environment) which are as follows:
- Financial resources
- Human resources
- Material resources
- Non-material resources (information, knowledge)
VRIO analysis is a complement to a PESTLE analysis and is used to assess the situation inside the organization – its resources, their competitive implication and possible potential for improvement in the given area or for a given resource.
Organizations should look inside the company to find the sources of competitive advantage instead of looking at the competitive environment.
The key concepts within this view are therefore Firm Resources and Sustainable Competitive Advantage.
Firm resources can be defined as ‘all assets, capabilities, organizational processes, firm attributes, information and knowledge controlled by a firm that enables it to improve its efficiency and effectiveness’.
Resources are often classified into categories such as tangible (e.g. equipment, machinery, land, buildings and cash) and intangible (e.g. trademarks, brand reputation, patents and licenses) or physical, human and organizational resources.
In order for companies to transform these resources into sustainable competitive advantage, resources must have four attributes that can be summarized into the VRIO framework.
1. Valuable
Do capabilities exist that are vaued by customers and enable the organization to respond to environmental opportunities or threats?
Resources must be valuable such that they enable a firm to implement strategies that improve a firm’s efficiency. If none of the resources possessed by a firm are considered valuable, the firm is likely to have a competitive disadvantage.
2. Rare
Do capabilities exist that no (or few) competitors possess?
Resources must be rare such that they may only be acquired by one or few companies. If a certain valuable resource is possessed by a large amount of players in the industry, each of the players has a capability to exploit the resource in the same way, thereby implementing a common strategy that gives none of the players a competitive advantage. Such a situation is indicated as competitive parity or competitive equality.
3. Inimitable
Are capabilities difficult and costly for competitors to obtain and imitate?
Although valuable and rare resources may help companies to engage in strategies that other firms cannot pursue since the other firms lack the relevant resources, it is no guarantee for long-term competitive advantage.
It may give the company a first-mover advantage but competitors will probably try to imitate these resources. Another criteria that resources should meet is therefore that they should be hard and costly to imitate or substitute.
4. Organization-wide supported
Is the organisation appropriately organised to exploit the capabilities?
The resources themselves do not create any advantage for a company if the company is not organized in a way to adequately exploit these resources and capture the value from them.
The company therefore needs the capability to assemble and coordinate resources effectively.
Without the correct organization to acquire, use and monitor the resources involved, even companies with valuable, rare and imperfectly imitable resources will not be able to create a sustainable competitive advantage.
VRIO attributes and the resulting advantages the company has in different situations.
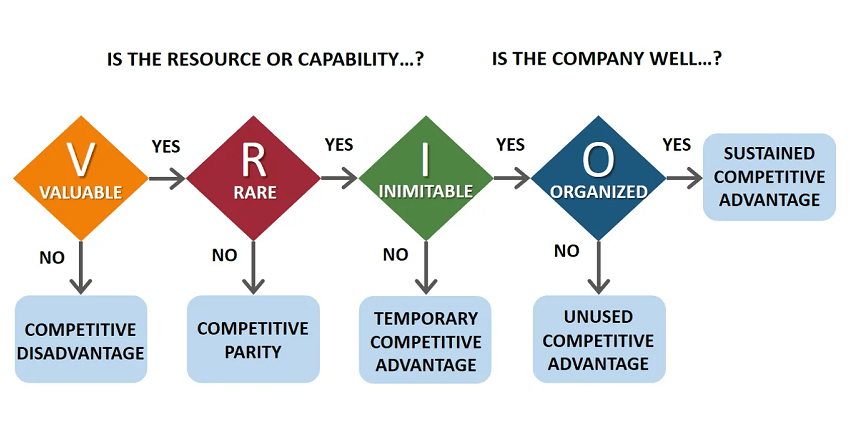
When all four resource attributes are present, the company has a distinctive competence that can be used as source of sustainable competitive advantage.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.